Cardiovascular disease risk factor profiles in children with celiac disease on gluten-free diets
- PMID: 24039358
- PMCID: PMC3769902
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5658
Cardiovascular disease risk factor profiles in children with celiac disease on gluten-free diets
Abstract
Aim: To describe the cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors in a population of children with celiac disease (CD) on a gluten-free diet (GFD).
Methods: This cross-sectional multicenter study was performed at Schneider Children's Medical Center of Israel (Petach Tiqva, Israel), and San Paolo Hospital (Milan, Italy). We enrolled 114 CD children in serologic remission, who were on a GFD for at least one year. At enrollment, anthropometric measurements, blood lipids and glucose were assessed, and compared to values at diagnosis. The homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance was calculated as a measure of insulin resistance.
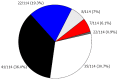
Results: Three or more concomitant CVD risk factors [body mass index, waist circumference, low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, blood pressure and insulin resistance] were identified in 14% of CD subjects on a GFD. The most common CVD risk factors were high fasting triglycerides (34.8%), elevated blood pressure (29.4%), and high concentrations of calculated LDL cholesterol (24.1%). On a GFD, four children (3.5%) had insulin resistance. Fasting insulin and HOMA-IR were significantly higher in the Italian cohort compared to the Israeli cohort (P < 0.001). Children on a GFD had an increased prevalence of borderline LDL cholesterol (24%) when compared to values (10%) at diagnosis (P = 0.090). Trends towards increases in overweight (from 8.8% to 11.5%) and obesity (from 5.3% to 8.8%) were seen on a GFD.
Conclusion: This report of insulin resistance and CVD risk factors in celiac children highlights the importance of CVD screening, and the need for dietary counseling targeting CVD prevention.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease risk factors; Celiac disease; Children; Cholesterol; Gluten-free diet; Hyperlipidemia; Insulin resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Fasano A, Araya M, Bhatnagar S, Cameron D, Catassi C, Dirks M, Mearin ML, Ortigosa L, Phillips A. Federation of International Societies of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition consensus report on celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008;47:214–219. - PubMed
-
- NIH Consensus Development Conference on Celiac Disease. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2004;21:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Green PH, Cellier C. Celiac disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1731–1743. - PubMed
-
- Green PH, Jabri B. Coeliac disease. Lancet. 2003;362:383–391. - PubMed
-
- Green PH. The many faces of celiac disease: clinical presentation of celiac disease in the adult population. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:S74–S78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

