Female pattern alopecia: current perspectives
- PMID: 24039457
- PMCID: PMC3769411
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S49337
Female pattern alopecia: current perspectives
Abstract
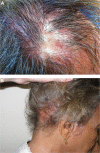
Hair loss is a commonly encountered problem in clinical practice, with men presenting with a distinctive pattern involving hairline recession and vertex balding (Norwood-Hamilton classification) and women exhibiting diffuse hair thinning over the crown (increased part width) and sparing of the frontal hairline (Ludwig classification). Female pattern hair loss has a strikingly overwhelming psychological effect; thus, successful treatments are necessary. Difficulty lies in successful treatment interventions, as only two medications - minoxidil and finasteride - are approved for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia, and these medications offer mediocre results, lack of a permanent cure, and potential complications. Hair transplantation is the only current successful permanent option, and it requires surgical procedures. Several other medical options, such as antiandrogens (eg, spironolactone, oral contraceptives, cyproterone, flutamide, dutasteride), prostaglandin analogs (eg, bimatoprost, latanoprost), and ketoconazole are reported to be beneficial. Laser and light therapies have also become popular despite the lack of a profound benefit. Management of expectations is crucial, and the aim of therapy, given the current therapeutic options, is to slow or stop disease progression with contentment despite patient expectations of permanent hair regrowth. This article reviews current perspectives on therapeutic options for female pattern hair loss.
Keywords: androgenetic alopecia; antiandrogens; female pattern hair loss; finasteride; minoxidil; spironolactone.
Figures



References
-
- Olsen EA, Reed KB, Cacchio PB, Caudill L. Iron deficiency in female pattern hair loss, chronic telogen effluvium, and control groups. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63(6):991–999. - PubMed
-
- Norwood OT. Incidence of female androgenetic alopecia (female pattern alopecia) Dermatol Surg. 2001;27(1):53–54. - PubMed
-
- Birch MP, Messenger JF, Messenger AG. Hair density, hair diameter and the prevalence of female pattern hair loss. Br J Dermatol. 2001;144(2):297–304. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez ME, Cantatore-Francis J, Orlow SJ. Androgenetic alopecia in the paediatric population: a retrospective review of 57 patients. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163(2):378–385. - PubMed
-
- Cash TF, Price VH, Savin RC. Psychological effects of androgenetic alopecia on women: comparisons with balding men and with female control subjects. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993;29(4):568–575. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

