Viral membrane fusion and nucleocapsid delivery into the cytoplasm are distinct events in some flaviviruses
- PMID: 24039574
- PMCID: PMC3764215
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003585
Viral membrane fusion and nucleocapsid delivery into the cytoplasm are distinct events in some flaviviruses
Abstract
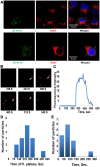
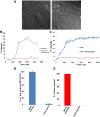
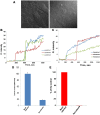
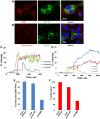
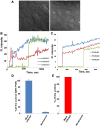
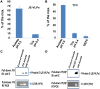
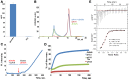
Flaviviruses deliver their genome into the cell by fusing the viral lipid membrane to an endosomal membrane. The sequence and kinetics of the steps required for nucleocapsid delivery into the cytoplasm remain unclear. Here we dissect the cell entry pathway of virions and virus-like particles from two flaviviruses using single-particle tracking in live cells, a biochemical membrane fusion assay and virus infectivity assays. We show that the virus particles fuse with a small endosomal compartment in which the nucleocapsid remains trapped for several minutes. Endosomal maturation inhibitors inhibit infectivity but not membrane fusion. We propose a flavivirus cell entry mechanism in which the virus particles fuse preferentially with small endosomal carrier vesicles and depend on back-fusion of the vesicles with the late endosomal membrane to deliver the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm. Virus entry modulates intracellular calcium release and phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate kinase signaling. Moreover, the broadly cross-reactive therapeutic antibody scFv11 binds to virus-like particles and inhibits fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Morita E, Sundquist WI (2004) Retrovirus budding. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20: 395–425. - PubMed
-
- Gruenberg J (2001) The endocytic pathway: a mosaic of domains. Nature reviews 2: 721–730. - PubMed
-
- Lemichez E, Bomsel M, Devilliers G, vanderSpek J, Murphy JR, et al. (1997) Membrane translocation of diphtheria toxin fragment A exploits early to late endosome trafficking machinery. Molecular microbiology 23: 445–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

