Myocardial injection of apelin-overexpressing bone marrow cells improves cardiac repair via upregulation of Sirt3 after myocardial infarction
- PMID: 24039710
- PMCID: PMC3765164
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071041
Myocardial injection of apelin-overexpressing bone marrow cells improves cardiac repair via upregulation of Sirt3 after myocardial infarction
Abstract
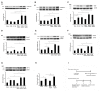
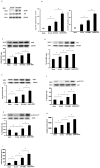
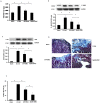
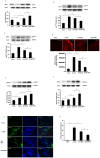
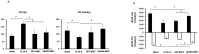
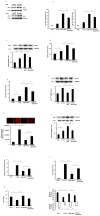
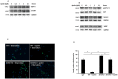
Our previous study shows that treatment with apelin increases bone marrow cells (BMCs) recruitment and promotes cardiac repair after myocardial infarction (MI). The objective of this study was to investigate whether overexpression of apelin in BMCs improved cell therapy and accelerated cardiac repair and functional recovery in post-MI mice. Mouse myocardial infarction was achieved by coronary artery ligation and BMCs overexpressing apelin (apelin-BMCs) or GFP (GFP-BMCs) were injected into ischemic area immediately after surgery. In vitro, exposure of cultured BMCs to apelin led to a gradual increase in SDF-1á and CXCR4 expression. Intramyocardial delivery of apelin-BMCs in post-MI mice resulted in a significant increase number of APJ⁺/c-kit⁺/Sca1⁺ cells in the injected area compared to GFP-BMCs treated post-MI mice. Treatment with apelin-BMCs increased expression of VEGF, Ang-1 and Tie-2 in post-MI mice. Apelin-BMCs treatment also significantly increased angiogenesis and attenuated cardiac fibrosis formation in post-MI mice. Most importantly, treatment with apelin-BMCs significantly improved left ventricular (LV) systolic function in post-MI mice. Mechanistically, Apelin-BMCs treatment led to a significant increase in Sirtuin3 (Sirt3) expression and reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation. Treatment of cultured BMCs with apelin also increased Notch3 expression and Akt phosphorylation. Apelin treatment further attenuated stress-induced apoptosis whereas knockout of Sirt3 abolished anti-apoptotic effect of apelin in cultured BMCs. Moreover, knockout of Sirt3 significantly attenuated apelin-BMCs-induced VEGF expression and angiogenesis in post-MI mice. Knockout of Sirt3 further blunted apelin-BMCs-mediated improvement of cardiac repair and systolic functional recovery in post-MI mice. These data suggest that apelin improves BMCs therapy on cardiac repair and systolic function in post-MI mice. Upregulation of Sirt3 may contribute to the protective effect of apelin-BMCs therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sirt3 is essential for apelin-induced angiogenesis in post-myocardial infarction of diabetes.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Jan;19(1):53-61. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12453. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25311234 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin-13 increases myocardial progenitor cells and improves repair postmyocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Sep 1;303(5):H605-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00366.2012. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22752632 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Sirt3 limits bone marrow cell-mediated angiogenesis and cardiac repair in post-myocardial infarction.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 5;9(9):e107011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107011. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25192254 Free PMC article.
-
Local activation of cardiac stem cells for post-myocardial infarction cardiac repair.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Nov;16(11):2549-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01589.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22613044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravascularly Deliverable Biomaterial Platforms for Tissue Repair and Regeneration Post-Myocardial Infarction.Adv Mater. 2024 Oct;36(43):e2300603. doi: 10.1002/adma.202300603. Epub 2023 Oct 29. Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 36989469 Review.
Cited by
-
Elabela-apelin receptor signaling pathway is functional in mammalian systems.Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 2;5:8170. doi: 10.1038/srep08170. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25639753 Free PMC article.
-
Potential clinical biomarkers and perspectives in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023 Mar 4;15(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13098-023-00998-y. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2023. PMID: 36871006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microvascular Rarefaction and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019 Feb 28;6:15. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00015. eCollection 2019. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 30873415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirt3 is essential for apelin-induced angiogenesis in post-myocardial infarction of diabetes.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Jan;19(1):53-61. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12453. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25311234 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of apelin-12 in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction with different renal function: a prospective observational study.BMJ Open. 2017 Nov 16;7(11):e018595. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018595. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29150476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schachinger V, Assmus B, Britten MB, Honold J, Lehmann R, et al. (2004) Transplantation of progenitor cells and regeneration enhancement in acute myocardial infarction: final one-year results of the TOPCARE-AMI Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 44: 1690–1699. - PubMed
-
- Britten MB, Abolmaali ND, Assmus B, Lehmann R, Honold J, et al. (2003) Infarct remodeling after intracoronary progenitor cell treatment in patients with acute myocardial infarction (TOPCARE-AMI): mechanistic insights from serial contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 108: 2212–2218. - PubMed
-
- Hu CH, Li ZM, Du ZM, Zhang AX, Rana JS, et al. (2010) Expanded human cord blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells salvage infarcted myocardium in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37: 551–556. - PubMed
-
- Cho J, Zhai P, Maejima Y, Sadoshima J (2011) Myocardial injection with GSK-3beta-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Circ Res 108: 478–489 CIRCRESAHA.110.229658 [pii]; doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.229658 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

