Ficolin-2 defends against virulent Mycobacteria tuberculosis infection in vivo, and its insufficiency is associated with infection in humans
- PMID: 24040095
- PMCID: PMC3767610
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073859
Ficolin-2 defends against virulent Mycobacteria tuberculosis infection in vivo, and its insufficiency is associated with infection in humans
Abstract
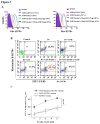
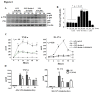
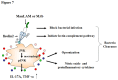
Human ficolin-2 (ficolin-2/P35) is a lectin complement pathway activator that is present in normal human plasma and is associated with infectious diseases; however, little is known regarding the roles and mechanisms of ficolin-2 during Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. Here, we describe our novel findings that the ficolin-2 serum levels of 107 pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) patients were much lower compared with 107 healthy controls. In vitro analysis showed that ficolin-2 bound to the virulent Mtb H37Rv strain much more strongly than to the non-virulent M. bovis BCG and M. smegmatis. Ficolin-2 bound to the surface glycolipid portion of H37Rv and blocked H37Rv infection in human lung A549 cells. Opsonophagocytosis was also promoted by ficolin-2. Importantly, we found that administration of exogenous ficolin-2 had a remarkable protective effect against virulent Mtb H37Rv infection in both C57BL/6J and BALB/c mice. Ficolin-A (a ficolin-2-like molecule in mouse) knockout mice exhibited increased susceptibility to H37Rv infection. We further demonstrated that ficolin-2 could defend against virulent Mtb H37Rv infection at least partially by activating JNK phosphorylation and stimulating the secretion of interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-17, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and nitric oxide (NO) production by macrophages. Our data provide a new immunotherapeutic strategy against TB based on the innate immune molecule ficolin-2 and indicate that ficolin-2 insufficiency is associated with higher susceptibility to infection in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Integrative Analysis of Human Macrophage Inflammatory Response Related to Mycobacterium tuberculosis Virulence.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 28;12:668060. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.668060. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276658 Free PMC article.
-
A CD4+CD161+ T-Cell Subset Present in Unexposed Humans, Not Tb Patients, Are Fast Acting Cells That Inhibit the Growth of Intracellular Mycobacteria Involving CD161 Pathway, Perforin, and IFN-γ/Autophagy.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 26;12:599641. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.599641. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33732233 Free PMC article.
-
Selection and identification of specific glycoproteins and glycan biomarkers of macrophages involved in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2017 May;104:95-106. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2017.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2017. PMID: 28454656
-
Lipoarabinomannan, and its related glycolipids, induce divergent and opposing immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis depending on structural diversity and experimental variations.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016 Jan;96:120-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016. PMID: 26586646 Review.
-
Chemical approaches to unraveling the biology of mycobacteria.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 May 18;30(5):420-435. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.04.014. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37207631 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ficolins and infectious diseases.Virol Sin. 2014 Feb;29(1):25-32. doi: 10.1007/s12250-014-3421-2. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Virol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24452543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of low ficolin-2 concentration in cord serum with respiratory distress syndrome in preterm newborns.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 17;14:1107063. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1107063. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36733481 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Complement System and the Immune Response to Tuberculosis Infection.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Jan 20;57(2):84. doi: 10.3390/medicina57020084. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 33498555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid and efficient purification of ficolin-2 using a disposable CELLine bioreactor.J Immunol Methods. 2015 Sep;424:106-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 May 30. J Immunol Methods. 2015. PMID: 26021447 Free PMC article.
-
MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs) and infectious diseases.Mol Immunol. 2015 Sep;67(1):85-100. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.03.245. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25862418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shah NS, Pratt R, Armstrong L, Robison V, Castro KG et al. (2008) Extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in the United States, 1993-2007. JAMA 300: 2153-2160. doi:10.1001/jama.300.18.2153. PubMed: 19001626. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Golub JE, Durovni B, King BS, Cavalacante SC, Pacheco AG et al. (2008) Recurrent tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. AIDS 22: 2527-2533. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e328311ac4e. PubMed: 19005276. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fujita T (2002) Evolution of the lectin-complement pathway and its role in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2: 346-353. doi:10.1038/nri800. PubMed: 12033740. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fujita T, Matsushita M, Endo Y (2004) The lectin-complement pathway--its role in innate immunity and evolution. Immunol Rev 198: 185-202. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.0123.x. PubMed: 15199963. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Sato Y, Matsushita M, Fujita T (1996) Cloning and characterization of the human lectin P35 gene and its related gene. Genomics 36: 515-521. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0497. PubMed: 8884275. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

