Status epilepticus induces vasogenic edema via tumor necrosis factor-α/ endothelin-1-mediated two different pathways
- PMID: 24040253
- PMCID: PMC3764062
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074458
Status epilepticus induces vasogenic edema via tumor necrosis factor-α/ endothelin-1-mediated two different pathways
Abstract
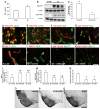
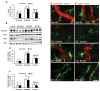
Status epilepticus (SE) induces vasogenic edema in the piriform cortex with disruptions of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). However, the mechanisms of vasogenic edema formation following SE are still unknown. Here we investigated the endothelin B (ETB) receptor-mediated pathway of SE-induced vasogenic edema. Following SE, the release of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) stimulated endothelin-1 (ET-1) release and expression in neurons and endothelial cells. In addition, TNF-α-induced ET-1 increased BBB permeability via ETB receptor-mediated endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation in endothelial cells. ETB receptor activation also increased intracellular reactive oxygen species by NADPH oxidase production in astrocytes. These findings suggest that SE results in BBB dysfunctions via endothelial-astroglial interactions through the TNF-α-ET-1-eNOS/NADPH oxidase pathway, and that these ETB receptor-mediated interactions may be an effective therapeutic strategy for vasogenic edema in various neurological diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Marmarou A (2007) A review of progress in understanding the pathophysiology and treatment of brain edema. Neurosurg Focus 22: E1. doi:10.3171/foc.2007.22.3.1. PubMed: 17613227. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nitsch C, Suzuki R, Fujiwara K, Klatzo I (1985) Incongruence of regional cerebral blood flow increase and blood-brain barrier opening in rabbits at the onset of seizures induced by bicuculline, methoxypyridoxine, and kainic acid. J Neurol Sci 67: 67-79. doi:10.1016/0022-510X(85)90023-1. PubMed: 3981213. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seiffert E, Dreier JP, Ivens S, Bechmann I, Tomkins O et al. (2004) Lasting blood-brain barrier disruption induces epileptic focus in the rat somatosensory cortex. J Neurosci 24: 7829-7836. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1751-04.2004. PubMed: 15356194. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim JE, Yeo SI, Ryu HJ, Kim MJ, Kim DS et al. (2010) Astroglial loss and edema formation in the rat piriform cortex and hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. J Comp Neurol 518: 4612-4628. doi:10.1002/cne.22482. PubMed: 20886625. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sheen SH, Kim JE, Ryu HJ, Yang Y, Choi KC et al. (2011) Decrease in dystrophin expression prior to disruption of brain-blood barrier within the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. Brain Res 1369: 173-183. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.10.080. PubMed: 21029730. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

