The rab11 effector protein FIP1 regulates adiponectin trafficking and secretion
- PMID: 24040321
- PMCID: PMC3770573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074687
The rab11 effector protein FIP1 regulates adiponectin trafficking and secretion
Abstract
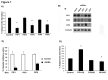
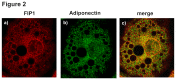
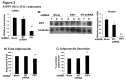
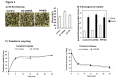
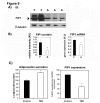
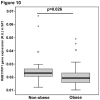
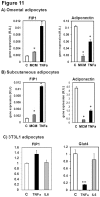
Adiponectin is an adipokine secreted by white adipocytes involved in regulating insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. Secretion of adiponectin in adipocytes relies on the endosomal system, however, the intracellular machinery involved in mediating adiponectin release is unknown. We have previously reported that intracellular adiponectin partially compartmentalizes with rab 5 and rab11, markers for the early/sorting and recycling compartments respectively. Here we have examined the role of several rab11 downstream effector proteins (rab11 FIPs) in regulating adiponectin trafficking and secretion. Overexpression of wild type rab11 FIP1, FIP3 and FIP5 decreased the amount of secreted adiponectin expressed in HEK293 cells, whereas overexpression of rab11 FIP2 or FIP4 had no effect. Furthermore shRNA-mediated depletion of FIP1 enhanced adiponectin release whereas knock down of FIP5 decreased adiponectin secretion. Knock down of FIP3 had no effect. In 3T3L1 adipocytes, endogenous FIP1 co-distributed intracellularly with endogenous adiponectin and FIP1 depletion enhanced adiponectin release without altering insulin-mediated trafficking of the glucose transporter Glut4. While adiponectin receptors internalized with transferrin receptors, there were no differences in transferrin receptor recycling between wild type and FIP1 depleted adipocytes. Consistent with its inhibitory role, FIP1 expression was decreased during adipocyte differentiation, by treatment with thiazolidinediones, and with increased BMI in humans. In contrast, FIP1 expression increased upon exposure of adipocytes to TNFα. In all, our findings identify FIP1 as a novel protein involved in the regulation of adiponectin trafficking and release.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
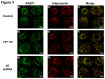
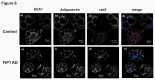
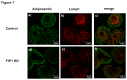
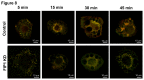
References
-
- Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM (1996) AdipoQ is a Novel Adipose-specific Gene Dysregulated in Obesity. J Biol Chem 271: 10697-10703. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.18.10697. PubMed: 8631877. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF (1995) A Novel Serum Protein Similar to C1q Produced exclusively in Adipocytes. J Biol Chem 270: 26746-26749. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.45.26746. PubMed: 7592907. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y et al. (1996) cDNA cloning and Expression of a ovel Adipose Specific Collagen-like Factor, apM1 (Adipose Most Abundant Gene Transcript 1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 221: 286-289. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1996.0587. PubMed: 8619847. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K et al. (2001) The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med 7: 941-945. doi:10.1038/90984. PubMed: 11479627. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berg A, Combs T, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE (2001) The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med 7: 847-853. doi:10.1038/89977. PubMed: 11433351. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

