Transcriptome analysis of encystation in Entamoeba invadens
- PMID: 24040350
- PMCID: PMC3770568
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074840
Transcriptome analysis of encystation in Entamoeba invadens
Abstract
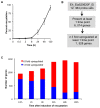
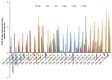
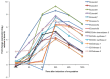
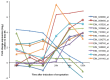
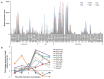
Encystation is an essential differentiation process for the completion of the life cycle of a group of intestinal protozoa including Entamoeba histolytica, the causative agent of intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis. However, regulation of gene expression during encystation is poorly understood. To comprehensively understand the process at the molecular level, the transcriptomic profiles of E. invadens, which is a related reptilian species that causes an invasive disease similar to that of E. histolytica, was investigated during encystation. Using a custom-generated Affymetrix platform microarray, we performed time course (0.5, 2, 8, 24, 48, and 120 h) gene expression analysis of encysting E. invadens. ANOVA analysis revealed that a total of 1,528 genes showed ≥3 fold up-regulation at one or more time points, relative to the trophozoite stage. Of these modulated genes, 8% (116 genes) were up-regulated at the early time points (0.5, 2 and 8h), while 63% (962 genes) were up-regulated at the later time points (24, 48, and 120 h). Twenty nine percent (450 genes) are either up-regulated at 2 to 5 time points or constitutively up-regulated in both early and late stages. Among the up-regulated genes are the genes encoding transporters, cytoskeletal proteins, proteins involved in vesicular trafficking (small GTPases), Myb transcription factors, cysteine proteases, components of the proteasome, and enzymes for chitin biosynthesis. This study represents the first kinetic analysis of gene expression during differentiation from the invasive trophozoite to the dormant, infective cyst stage in Entamoeba. Functional analysis on individual genes and their encoded products that are modulated during encystation may lead to the discovery of targets for the development of new chemotherapeutics that interfere with stage conversion of the parasite.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Stanley SL (2003) Amebiasis. Lancet 361: 1025-1034. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12830-9. PubMed: 12660071. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nozaki T, Kobayashi S, Takeuchi T, Haghighi A (2005) The diversity of clinical isolates of Entamoeba histolytica in Japan. Arch Med Res 37: 276-278. - PubMed
-
- Clark CG, Alsmark UC, Tazreiter M, Saito-Nakano Y, Ali V et al. (2007) Structure and content of the Entamoeba histolytica genome. Adv Parasitol 65: 51–190. doi:10.1016/S0065-308X(07)65002-7. PubMed: 18063096. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eichinger D (1997) Encystation of Entamoeba parasites. Bioessays 19: 633-638. doi:10.1002/bies.950190714. PubMed: 9230696. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

