The contribution of Orai(CRACM)1 and Orai(CRACM)2 channels in store-operated Ca2+ entry and mediator release in human lung mast cells
- PMID: 24040356
- PMCID: PMC3769304
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074895
The contribution of Orai(CRACM)1 and Orai(CRACM)2 channels in store-operated Ca2+ entry and mediator release in human lung mast cells
Abstract
Background: The influx of extracellular Ca(2+) into mast cells is critical for the FcεR1-dependent release of preformed granule-derived mediators and newly synthesised autacoids and cytokines. The Orai(CRACM) ion channel family provide the major pathway through which this Ca(2+) influx occurs. However the individual role of each of the three members of the Orai channel family in Ca(2+) influx and mediator release has not been defined in human mast cells.
Objective: To assess whether there might be value in targeting individual Orai family members for the inhibition of FcεRI-dependent human lung mast cells (HLMC) mediator release.
Methods: We used an adenoviral delivery system to transduce HLMCs with shRNAs targeted against Orai1 and Orai2 or with cDNAs directing the expression of dominant-negative mutations of the three known Orai channels.
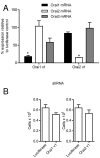
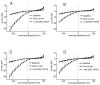
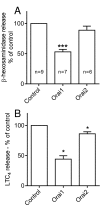
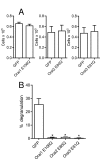
Results: shRNA-mediated knockdown of Orai1 resulted in a significant reduction of approximately 50% in Ca(2+) influx and in the release of β-hexosaminidase (a marker of degranulation) and newly synthesized LTC4 in activated HLMCs. In contrast shRNA knockdown of Orai2 resulted in only marginal reductions of Ca(2+) influx, degranulation and LTC4 release. Transduced dominant-negative mutants of Orai1, -2 and -3 markedly reduced Orai currents and completely inhibited HLMC degranulation suggesting that Orai channels form heteromultimers in HLMCs, and that Orai channels comprise the dominant Ca(2+) influx pathway following FceRI-dependent HLMC activation. Inhibition of Orai currents did not alter HLMC survival. In addition we observed a significant down-regulation of the level of CRACM3 mRNA transcripts together with a small increase in the level of CRACM1 and CRACM2 transcripts following a period of sustained HLMC activation.
Conclusion and clinical relevance: Orai1 plays an important role in Ca(2+) influx and mediator release from HLMCs. Strategies which target Orai1 will effectively inhibit FcεRI-dependent HLMC activation, but spare off-target inhibition of Orai2 in other cells and body systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bradding P, Walls AF, Holgate ST (2006) The role of the mast cell in the pathophysiology of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 117: 1277-1284. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2006.02.039. PubMed: 16750987. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Parekh AB, Putney JW Jr (2005) Store-operated calcium channels. Physiol Rev 85: 757-810. doi:10.1152/physrev.00057.2003. PubMed: 15788710. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hoth M, Penner R (1992) Depletion of intracellular calcium stores activates a calcium current in mast cells. Nature 355: 353-356. doi:10.1038/355353a0. PubMed: 1309940. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang SL, Yu Y, Roos J, Kozak JA, Deerinck TJ et al. (2005) STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature 437: 902-905. doi:10.1038/nature04147. PubMed: 16208375. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

