Health risk assessment of heavy metals in rice to the population in Zhejiang, China
- PMID: 24040375
- PMCID: PMC3765370
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075007
Health risk assessment of heavy metals in rice to the population in Zhejiang, China
Abstract
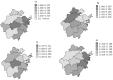
Environmental pollution with toxic heavy metals can lead to the possible contamination of the rice. Selected metals (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) and their accumulation in rice collected from Zhejiang, China were analyzed to evaluate the potential health risk to the local adults and children. The mean levels found in rice were as follows: As, 0.080 mg/kg; Cd, 0.037 mg/kg; Hg, 0.005 mg/kg; Pb, 0.060 mg/kg. The estimated daily intakes (EDIs) were calculated in combination of the rice consumption data. The mean intakes of As, Cd, Hg and Pb through rice were estimated to be 0.49, 0.23, 0.03 and 0.37 µg/kg bw/day for adults, and 0.34, 0.29, 0.04 and 0.47 µg/kg bw/day for children. The 97.5th percentile (P97.5) daily intakes of As, Cd, Hg and Pb were 1.02, 0.64, 0.37 and 1.26 µg/kg bw/day for adults, and 0.63, 0.83, 0.47 and 1.63 µg/kg bw/day for children. The risk assessment in mean levels showed that health risk associated with these elements through consumption of rice was absent. However, estimates in P97.5 level of Cd and Pb for children, and Hg for adults have exceeded the respective safe limits.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- FAOSTAT (2011) FAO Statistical databases. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Available: http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx. Accessed 1 May 2013.
-
- UNCTAD (2011) United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. Available: http://www.unctad.org/infocomm/anglais/rice/market.htm2011. Accessed 1 May 2013.
-
- Fu J, Zhou Q, Liu J, Liu W, Wang T, et al. (2008) High levels of heavy metals in rice (Oryza sativa L.) from a typical E-waste recycling area in southeast China and its potential risk to human health. Chemosphere 71: 1269–1275 doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.065 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao K, Liu X, Xu J, Selim HM (2010) Heavy metal contaminations in a soil–rice system: Identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields. J Hazard Material 181: 778–787 doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.081 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang X, Wang H, Zhou J, Ma C, Du C, et al. (2009) Risk assessment of potentially toxic element pollution in soils and rice (Oryza sativa) in a typical area of the Yangtze River Delta. Environ Pollut 157: 2542–2549 doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.03.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials