Protein phosphatase 1 β paralogs encode the zebrafish myosin phosphatase catalytic subunit
- PMID: 24040418
- PMCID: PMC3770619
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075766
Protein phosphatase 1 β paralogs encode the zebrafish myosin phosphatase catalytic subunit
Abstract
Background: The myosin phosphatase is a highly conserved regulator of actomyosin contractility. Zebrafish has emerged as an ideal model system to study the in vivo role of myosin phosphatase in controlling cell contractility, cell movement and epithelial biology. Most work in zebrafish has focused on the regulatory subunit of the myosin phosphatase called Mypt1. In this work, we examined the critical role of Protein Phosphatase 1, PP1, the catalytic subunit of the myosin phosphatase.
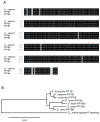
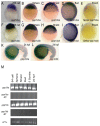
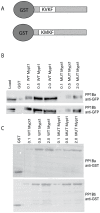
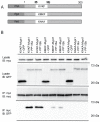
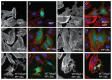
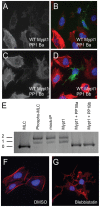
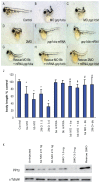
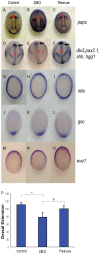
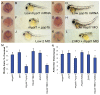
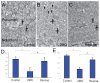
Methodology/principal findings: We observed that in zebrafish two paralogous genes encoding PP1β, called ppp1cba and ppp1cbb, are both broadly expressed during early development. Furthermore, we found that both gene products interact with Mypt1 and assemble an active myosin phosphatase complex. In addition, expression of this complex results in dephosphorylation of the myosin regulatory light chain and large scale rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton. Morpholino knock-down of ppp1cba and ppp1cbb results in severe defects in morphogenetic cell movements during gastrulation through loss of myosin phosphatase function.
Conclusions/significance: Our work demonstrates that zebrafish have two genes encoding PP1β, both of which can interact with Mypt1 and assemble an active myosin phosphatase. In addition, both genes are required for convergence and extension during gastrulation and correct dosage of the protein products is required.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Landsverk ML, Epstein HF (2005) Genetic analysis of myosin II assembly and organization in model organisms. Cell Mol Life Sci 62: 2270-2282. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5176-2. PubMed: 16142426. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vicente-Manzanares M, Ma X, Adelstein RS, Horwitz AR (2009) Non-muscle myosin II takes centre stage in cell adhesion and migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 778-790. doi:10.1038/nrm2786. PubMed: 19851336. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hirano K, Derkach DN, Hirano M, Nishimura J, Kanaide H (2003) Protein kinase network in the regulation of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain. Mol Cell Biochem 248: 105-114. doi:10.1023/A:1024180101032. PubMed: 12870661. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haystead TA (2005) ZIP kinase, a key regulator of myosin protein phosphatase 1. Cell Signal 17: 1313-1322. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.05.008. PubMed: 16005610. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Grassie ME, Moffat LD, Walsh MP, Macdonald JA (2011) The myosin phosphatase targeting protein (MYPT) family: A regulated mechanism for achieving substrate specificity of the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase type 1delta. Arch Biochem Biophys. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

