Mechanism of action of the novel aminomethylcycline antibiotic omadacycline
- PMID: 24041885
- PMCID: PMC3957880
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01066-13
Mechanism of action of the novel aminomethylcycline antibiotic omadacycline
Abstract
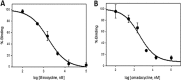
Omadacycline is a novel first-in-class aminomethylcycline with potent activity against important skin and pneumonia pathogens, including community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), β-hemolytic streptococci, penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Legionella. In this work, the mechanism of action for omadacycline was further elucidated using a variety of models. Functional assays demonstrated that omadacycline is active against strains expressing the two main forms of tetracycline resistance (efflux and ribosomal protection). Macromolecular synthesis experiments confirmed that the primary effect of omadacycline is on bacterial protein synthesis, inhibiting protein synthesis with a potency greater than that of tetracycline. Biophysical studies with isolated ribosomes confirmed that the binding site for omadacycline is similar to that for tetracycline. In addition, unlike tetracycline, omadacycline is active in vitro in the presence of the ribosomal protection protein Tet(O).
Figures


References
-
- Nelson ML, Ismail MY, McIntyre L, Bhatia B, Viski P, Hawkins P, Rennie G, Andorsky D, Messersmith D, Stapleton K, Dumornay J, Sheahan P, Verma AK, Warchol T, Levy SB. 2003. Versatile and facile synthesis of diverse semisynthetic tetracycline derivatives via Pd-catalyzed reactions. J. Org. Chem. 68:5838–5851. 10.1021/jo030047d - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

