Global transcriptome analysis of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in response to innate immune cells
- PMID: 24042108
- PMCID: PMC3837966
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00819-13
Global transcriptome analysis of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in response to innate immune cells
Abstract
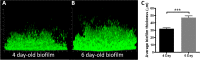
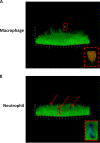
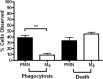
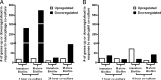
The potent phagocytic and microbicidal activities of neutrophils and macrophages are among the first lines of defense against bacterial infections. Yet Staphylococcus aureus is often resistant to innate immune defense mechanisms, especially when organized as a biofilm. To investigate how S. aureus biofilms respond to macrophages and neutrophils, gene expression patterns were profiled using Affymetrix microarrays. The addition of macrophages to S. aureus static biofilms led to a global suppression of the biofilm transcriptome with a wide variety of genes downregulated. Notably, genes involved in metabolism, cell wall synthesis/structure, and transcription/translation/replication were among the most highly downregulated, which was most dramatic at 1 h compared to 24 h following macrophage addition to biofilms. Unexpectedly, few genes were enhanced in biofilms after macrophage challenge. Unlike coculture with macrophages, coculture of S. aureus static biofilms with neutrophils did not greatly influence the biofilm transcriptome. Collectively, these experiments demonstrate that S. aureus biofilms differentially modify their gene expression patterns depending on the leukocyte subset encountered.
Figures
References
-
- Bronner S, Monteil H, Prevost G. 2004. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus: complexity and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 28:183–200 - PubMed
-
- Novick RP. 2003. Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 48:1429–1449 - PubMed
-
- Arciola CR, Campoccia D, Speziale P, Montanaro L, Costerton JW. 2012. Biofilm formation in Staphylococcus implant infections. A review of molecular mechanisms and implications for biofilm-resistant materials. Biomaterials 33:5967–5982 - PubMed
-
- Kiedrowski MR, Horswill AR. 2011. New approaches for treating staphylococcal biofilm infections. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1241:104–121 - PubMed
-
- Whitchurch CB, Tolker-Nielsen T, Ragas PC, Mattick JS. 2002. Extracellular DNA required for bacterial biofilm formation. Science 295:1487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

