Determination and pharmacokinetics of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in rats by ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 24043141
- PMCID: PMC6269943
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules180911452
Determination and pharmacokinetics of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in rats by ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
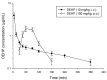
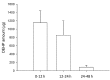
Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) is used to increase the flexibility of plastics for industrial products. However, the illegal use of the plasticizer DEHP in food and drinks has been reported in Taiwan in 2011. In order to assess the exact extent of the absorption of DEHP via the oral route, the aim of this study is to develop a reliable and validated ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method to evaluate the oral bioavailability of DEHP in rats. The optimal chromatographic separation of DEHP and butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP; used as internal standard) were achieved on a C₁₈ column. The mobile phase was consisted of 5 mM ammonium acetate-methanol (11:89, v/v) with a flow rate of 0.25 mL/min. The monitoring ion transitions were m/z 391.4 → 149.0 for DEHP and m/z 313.3 → 149.0 for BBP. The mean matrix effects of DEHP at low, medium and high concentrations were 94.5 ± 5.7% and 100.1 ± 2.3% in plasma and feces homogenate samples, respectively. In conclusion, the validated UPLC-MS/MS method is suitable for analyzing the rat plasma sample of DEHP and the oral bioavailability of DEHP was about 7% in rats.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of di-isononyl phthalate in freely moving rats by UPLC-MS/MS.Int J Pharm. 2013 Jun 25;450(1-2):36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.04.033. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Int J Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23618960
-
Urinary metabolomic profiling in rats exposed to dietary di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) using ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC/Q-TOF-MS).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Jul;24(20):16659-16672. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9091-5. Epub 2017 May 30. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28560624
-
Simultaneous determination of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and diisononylcyclohexane-1,2-dicarboxylate and their monoester metabolites in four labile blood products by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Mar 20;181:113063. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.113063. Epub 2019 Dec 23. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020. PMID: 31927338
-
Determination of five di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate metabolites in urine by UPLC-MS/MS, markers of blood transfusion misuse in sports.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012 Nov 1;908:113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.09.030. Epub 2012 Sep 21. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 23040990
-
Metabolism of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP): comparative study in juvenile and fetal marmosets and rats.J Toxicol Sci. 2012 Feb;37(1):33-49. doi: 10.2131/jts.37.33. J Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22293410
Cited by
-
Impact of Plasticizer on the Intestinal Epithelial Integrity and Tissue-Repairing Ability within Cells in the Proximity of the Human Gut Microbiome.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 25;20(3):2152. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20032152. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767519 Free PMC article.
-
Food Emulsifier Glycerin Monostearate Increases Internal Exposure Levels of Six Priority Controlled Phthalate Esters and Exacerbates Their Male Reproductive Toxicities in Rats.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 30;11(8):e0161253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161253. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27575856 Free PMC article.
-
Advancement in Determination of Phthalate Metabolites by Gas Chromatography Eliminating Derivatization Step.Front Chem. 2020 Jan 15;7:928. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00928. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32010672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanawa T., Muramatsu E., Asakawa K., Suzuki M., Tanaka M., Kawano K., Seki T., Juni K., Nakajima S. Investigation of the release behavior of diethylhexyl phthalate from the polyvinyl-chloride tubing for intravenous administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2000;210:109–115. doi: 10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00578-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Faouzi M.A., Khalfi F., Dine T., Luyckx M., Brunet C., Gressier B., Goudaliez F., Cazin M., Kablan J., Belabed A., et al. Stability, compatibility and plasticizer extraction of quinine injection added to infusion solutions and stored in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) containers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999;21:923–930. doi: 10.1016/S0731-7085(99)00204-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

