Intravenous immunoglobulin for treating sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock
- PMID: 24043371
- PMCID: PMC6516813
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001090.pub2
Intravenous immunoglobulin for treating sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock
Abstract
Background: Mortality from sepsis and septic shock remains high. Results of trials on intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) as adjunctive therapy for sepsis have been conflicting. This is an update of a Cochrane review that was originally published in 1999 and updated in 2002 and 2010.
Objectives: To estimate the effects of IVIG as adjunctive therapy in patients with bacterial sepsis or septic shock on mortality, bacteriological failure rates, and duration of stay in hospital.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2012, Issue 6), MEDLINE (1966 to December 2012), and EMBASE (1988 to December 2012). We contacted investigators in the field for unpublished data. The original search was performed in 1999 and updated in 2002 and 2008.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials comparing IVIG (monoclonal or polyclonal) with placebo or no intervention in patients of any age with bacterial sepsis or septic shock.
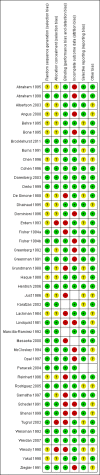
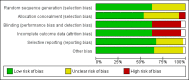
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed the studies for inclusion and undertook methodologic quality assessment and data abstraction. We conducted pre-specified subgroup analyses by type of immunoglobulin preparation.
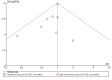
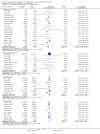
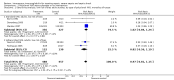
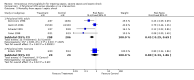
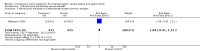
Main results: We included 43 studies that met our inclusion criteria in this updated review out of 88 potentially eligible studies. The studies included a large polyclonal IVIG trial in neonates that was concluded in 2011 and classified as ongoing in the 2010 version of this review. Pooled analysis of polyclonal and monoclonal IVIG was not done due to clinical heterogeneity. Subgroup analysis of 10 polyclonal IVIG trials (n = 1430) and seven trials on IgM-enriched polyclonal IVIG (n = 528) showed significant reductions in mortality in adults with sepsis compared to placebo or no intervention (relative risk (RR) 0.81; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.70 to 0.93 and RR 0.66; 95% CI 0.51 to 0.85, respectively). Subgroup analysis of polyclonal IVIG in neonates, which now includes the recently concluded large polyclonal IVIG trial, showed no significant reduction in mortality for standard IVIG (RR 1.00; 95% CI 0.92 to 1.08; five trials, n = 3667) and IgM-enriched polyclonal IVIG (RR 0.57; 95% CI 0.31 to 1.04; three trials, n = 164). Sensitivity analysis of trials with low risk of bias showed no reduction in mortality with polyclonal IVIG in adults (RR 0.97; 95% CI 0.81 to 1.15; five trials, n = 945) and neonates (RR 1.01; 95% CI 0.93 to 1.09; three trials, n = 3561). Mortality was not reduced among patients (eight trials, n = 4671) who received anti-endotoxin antibodies (RR 0.99; 95% CI 0.91 to1.06) while anti-cytokines (nine trials, n = 7893) demonstrated a marginal reduction in mortality (RR 0.92; 95% CI 0.86 to 0.97).
Authors' conclusions: Polyclonal IVIG reduced mortality among adults with sepsis but this benefit was not seen in trials with low risk of bias. Among neonates with sepsis, there is sufficient evidence that standard polyclonal IVIG, as adjunctive therapy, does not reduce mortality based on the inclusion of the large polyclonal IVIG trial on neonates. For Ig-M enriched IVIG, the trials on neonates and adults were small and the totality of the evidence is still insufficient to support a robust conclusion of benefit. Adjunctive therapy with monoclonal IVIGs remains experimental.
Conflict of interest statement
Marissa M Alejandria: none known
Mary Ann D Lansang: none known
Leonila F Dans: travel grant from Novartis to attend a meeting of pediatric rheumatologists to discuss the management of systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis in November 2012.
Jacinto Blas Mantaring III: Dr Mantaring is the chair of the National Institutes of Health Ethics review board and a member of the Technical review board, who receives an honorarium for reviewing studies and attending meetings. He is also asked by government agencies, WHO and pharmaceutical companies to give lectures, conduct workshops and prepare educational materials on a variety of topics mostly related to research methods, evidence‐based medicine and ethics as well as topics on neonatal care.
We certify that we have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with a direct financial interest in the subject matter of the review (for example through employment, consultancy, stock ownership, honoraria, expert testimony).
Figures















Update of
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin for treating sepsis and septic shock.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(1):CD001090. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001090. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 16;(9):CD001090. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001090.pub2. PMID: 11869591 Updated.
Comment in
-
[Treatment of sepsis and septic shock with immunoglobulins].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014 Jan;139(5):178. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1329177. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 24449349 German. No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abraham 1995 {published data only}
-
- Abraham E, Wunderink R, Silverman H, Perl TM, Nasraway S, Levy H, et al. Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with sepsis syndrome. A randomized, controlled double‐blind, multicenter clinical trial. TNF‐alpha MAb Sepsis Study group. JAMA 1995;273:934‐41. [PUBMED: 7884952] - PubMed
Abraham 1998 {published data only}
-
- Abraham E, Anzueto A, Gutierrez G, Tessler S, San Pedro G, Wunderink R, et al. Double‐blind randomized controlled trial of monoclonal antibody to human tumour necrosis factor in treatment of septic shock.NORASEPT II Study Group. Lancet 1998;351:929‐33. [PUBMED: 9734938] - PubMed
Albertson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Albertson TE, Panacek EA, MacArthur RD, Johnson SB, Benjamin E, Matsuchak G, et al. Multicenter evaluation of a human monoclonal antibody to Enterobacteriaceae common antigen in patients with Gram‐negative sepsis. Critical Care Medicine 2003;31:419‐27. [PUBMED: 12576946 ] - PubMed
Angus 2000 {published data only}
-
- Angus DC, Birmingham MC, Balk RA, Scannon PJ, Collins D, Kruse JA, et al. E5 murine monoclonal antiendotoxin antibody in gram‐negative sepsis: a randomized controlled trial. E5 Study Investigators. JAMA 2000;283:1723‐30. [PUBMED: 10755499] - PubMed
Behre 1995 {published data only}
-
- Behre G, Ostermann H, Schedel I, Helmerking M, Schiel X, Rothenburger M, et al. Endotoxin concentrations and therapy with polyclonal IgM‐enriched immunoglobulins in neutropenic cancer patients with sepsis syndrome: Pilot study and interim analysis of a randomized trial. Antiinfective Drugs and Chemotherapy 1995;13:129‐34. [CENTRAL: CN‐00168897; EMBASE: 1996075665]
Bone 1995 {published data only}
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Fein AM, Perl TM, Wenzel RP, Reines HD, et al. A second large controlled clinical study of E5, a monoclonal antibody to endotoxin: results of a prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial. The E5 Sepsis Study Group. Critical Care Medicine 1995;23:994‐1005. [PUBMED: 7774238] - PubMed
Brocklehurst 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- The INIS Collaborative Group. Treatment of neonatal sepsis with intravenous immune globulin. The New England Journal of Medicine 2011;365:1201‐11. - PubMed
-
- The INIS Study Collaborative Group. The INIS Study. International Neonatal Immunotherapy Study: Non‐specific intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for suspected or proven neonatal sepsis: an international, placebo‐controlled, multicentre randomised trial. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2008;8:1‐13. - PMC - PubMed
Burns 1991 {published data only}
-
- Burns ER, Lee V, Rubinstein A. Treatment of septic thrombocytopenia with immune globulin. Journal of Clinical Immunology 1991;11:363‐8. [PUBMED: 1761642] - PubMed
Chen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Chen JY. Intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of full term and premature newborns with sepsis. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association: Taiwan Yi Zhi 1996;11:839‐44. [PUBMED: 8990771] - PubMed
Cohen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Cohen J, Carlet J. INTERSEPT: an international, multicenter, placebo‐controlled‐trial of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor‐alpha in patients with sepsis. International Sepsis Trial Study Group. Critical Care Medicine 1996;24:1431‐40. [PUBMED: 8797612 ] - PubMed
Darenberg 2003 {published data only}
-
- Darenberg J, Ihendyane N, Sjölin J, Aufwerber E, Haidl S, Follin P, et al. StreptIg Study Group. Intravenous immunoglobulin G therapy in streptococcal toxic shock syndrome: a European randomized, double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2003;37:333‐40. [PUBMED: 12884156 ] - PubMed
Derkx 1999 {published data only}
-
- Derkx B, Wittes J, McCloskey R. Randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of HA‐1A, a human monoclonal antibody to endotoxin, in children with meningococcal septic shock. European Pediatric Meningococcal Septic Shock Trial Study Group. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1999;28:770‐7. [PUBMED: 10825037] - PubMed
De Simone 1988 {published data only}
-
- Simone C, Delogu G, Corbetta G. Intravenous immunoglobulins in association with antibiotics: a therapeutic trial in septic intensive care unit patients. Critical Care Medicine 1988;16:23‐6. [PUBMED: 3276446] - PubMed
Dhainaut 1995 {published data only}
-
- Dhainaut JF, Vincent JL, Richard C, Lejeune P, Martin C, Fierobe L, et al. CDP 571, a humanized antibody to human tumor necrosis factor alpha: safety, pharmacokinetics, immune response, and influence of the antibody on cytokine concentrations in patients with septic shock. CPD571 Sepsis Study Group. Critical Care Medicine 1995;23:1461‐9. [PUBMED: 7664546 ] - PubMed
Dominioni 1996 {published data only}
-
- Dominioni L, Bianchi V, Imperatori A, Minoia G, Dionigi R. High‐dose intravenous IgG for treatment of severe surgical infections. Digestive Surgery 1996;13:430‐4. [CENTRAL: CN‐00169903; PUBMED: 1996308558]
Erdem 1993 {published data only}
-
- Erdem G, Yurdakök M, Tekinalp G, Ersoy F. The use of IgM‐enriched intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of neonatal sepsis in preterm infants. The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 1993;35:277‐81. [PUBMED: 8160279] - PubMed
Fisher 1994a {published data only}
-
- Fisher CJ Jr, Slotman GJ, Opal SM, Pribble JP, Bone RC, Emmanuel G, et al. IL‐1RA Sepsis Syndrome Study Group. Initial evaluation of human recombinant interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of sepsis syndrome: a randomized open‐label, placebo‐controlled multicenter trial. Critical Care Medicine 1994;22:12‐21. [PUBMED: 8124953] - PubMed
Fisher 1994b {published data only}
-
- Fisher CJ Jr, Dhainaut JF, Opal SM, Pribble JP, Balk RA, Slotman GJ, et al. Recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of patients with sepsis syndrome: Results from a randomized double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Phase III rhIL‐1ra Sepsis Syndrome Study Group. JAMA 1994;271:1836‐43. - PubMed
Greenberg 1992 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg RN, Wilson KM, Kunz AY, Wedel NI, Gorelick KJ. Observations using antiendotoxin antibody (E5) as adjuvant therapy in humans with suspected with suspected serious, gram‐negative sepsis. Critical Care Medicine 1992;20:730‐5. [PUBMED: 1597023] - PubMed
Greenman 1991 {published data only}
-
- Greenman RL, Schein RM, Martin MA, Wenzel RP, MacIntyre NR, Emmanuel G, et al. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram‐negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. JAMA 1991;266:1097‐102. [PUBMED: 1865542] - PubMed
Grundmann 1988 {published data only}
-
- Grundmann R, Hornung M. Immunoglobulin therapy in patients with endotoxemia and postoperative sepsis ‐ a prospective randomized study. Progress in Clinical and Biological Research 1988;272:339‐49. [PUBMED: 3293080] - PubMed
Haque 1988 {published data only}
-
- Haque KN, Zaidi MH, Bahakim H. IgM‐enriched intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in neonatal sepsis. American Journal of Diseases of Childhood 1988;142:1293‐6. [PUBMED: 3195529] - PubMed
Hentrich 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hentrich M, Fehnle K, Ostermann H, Klenast J, Cornely O, Salat C, et al. IgMA‐enriched immunoglobulin in neutropenic patients with sepsis syndrome and septic shock: a randomized, controlled, multiple‐center trial. Critical Care Medicine 2006;34:1319‐25. [PUBMED: 16540956] - PubMed
Just 1986 {published data only}
-
- Just HM, Metzger M, Vogel W, Pelka RB. Effect of adjuvant immunoglobulin therapy in patients in a surgical intensive care unit. Results of a randomized controlled study [Einfluss einer adjuvanten Immunglobulintherapie auf Infektionen bei Patienten einer operativen Intensiv‐Therapie‐Station.]. Klinische Wochenschrift 1986;64:245‐56. [PUBMED: 3713101] - PubMed
Karatzas 2002 {published data only}
Lachman 1984 {published data only}
-
- Lachman E, Pitsoe SB, Gaffin SL. Anti‐lipopolysaccharide immunotherapy in management of septic shock of obstetric and gynecological origin. Lancet 1984;1:981‐3. [PUBMED: 6143965] - PubMed
Lindquist 1981 {published data only}
-
- Lindquist L, Lundbergh P, Maasing R. Pepsin‐treated human gamma globulin in bacterial infections. A randomized study in patients with septicemia and pneumonia. Vox Sanguinis 1981;40:329‐37. [PUBMED: 6166128 ] - PubMed
Mancilla‐Ramirez 1992 {published data only}
-
- Mancilla‐Ramírez J, González‐Yunes R, Castellanos‐Cruz C, García‐Roca P, Santos‐Preciado JI. Intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of neonatal septicemia [Inmunoglobulina intravenosa en el tratamiento de septicemia neonatal.]. Boletín Médico del Hospital Infantil de México 1992;49:4‐11. [PUBMED: 1304766] - PubMed
Masaoka 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Masaoka T, Hasegawa H, Takaku F, Mizoguchi H, Asano S, Ikeda Y, et al. The efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in combination therapy with antibiotics for severe infections. Japanese Journal of Chemotherapy 2000;48:199‐217. [CENTRAL: CN‐00418781; EMBASE: 2000159529]
McCloskey 1994 {published data only}
-
- MacCloskey RV, Straube RC, Sanders C, Smith SM, Smith CR. Treatment of septic shock with human monoclonal antibody HA‐1A. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. CHESS Trial Study Group. Annals of Internal Medicine 1994;121:1‐5. [PUBMED: 8198341] - PubMed
Opal 1997 {published data only}
-
- Opal SM, Fisher CJ, Dhainaut JF, Vincent JL, Brase R, Lowry SF, et al. Confirmatory interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: A phase III, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicenter trial. The Interleukin‐1 Receptor Antagonist Sepsis Investigator Group. Critical Care Medicine 1997;25:1115‐24. [PUBMED: 9233735] - PubMed
Panacek 2004 {published data only}
-
- Panacek EA, Marshall JC, Albertson TE, Johnson DH, Johnson S, MacArthur RD, et al. Monoclonal Anti‐TNF: Randomized Controlled Sepsis Study Investigators. Efficacy and safety of the monoclonal anti‐‐tumor necrosis factor antibody F(ab')2 fragment afelimomab in patients with severe sepsis and elevated interleukin‐6 levels. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32:2173‐82. [PUBMED: 15640628 ] - PubMed
Reinhart 1996 {published data only}
-
- Reinhart K, Wiegand‐Löhnert C, Grimminger F, Kaul M, Withington S, Treacher D, et al. Assessment of the safety and efficacy of the monoclonal anti‐tumor necrosis factor antibody‐fragment, MAK 195F, in patients with sepsis and septic shock: a multicenter, randomized, placebo‐controlled, dose ranging study. Critical Care Medicine 1996;24:733‐42. [PUBMED: 8706447] - PubMed
Rodriguez 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rodriguez A, Rello J, Neira J, Maskin B, Ceraso D, Vasta L, et al. Effects of high‐dose of intravenous immunoglobulin and antibiotics on survival for severe sepsis undergoing surgery. Shock 2005;23:298‐304. [PUBMED: 15803051 ] - PubMed
Samatha 1997 {published data only}
-
- Samatha S, Jalalu MP, Hegde RK, Vishwanath D, Maiya PP. Role of IgM‐enriched intravenous immunoglobulin as an adjuvant to antibiotics in neonatal sepsis. Karnataka Pediatric Journal 1997;11:1‐6.
Schedel 1991 {published data only}
-
- Schedel I, Dreikhausen U, Nentwig B, Höckenschnieder M, Rauthmann D, Balikcioglu S, et al. Treatment of Gram‐negative septic shock and an immunoglobulin preparation: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Critical Care Medicine 1991;10:1104‐13. [PUBMED: 1884609] - PubMed
Shenoi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Shenoi A, Nagesh NK, Maiya PP, Bhat SR, Subba Rao SD. Multicenter randomized placebo controlled trial of therapy with intravenous immunoglobulin in decreasing mortality due to neonatal sepsis. Indian Pediatrics 1999;36:1113‐8. [PUBMED: 10745332] - PubMed
Tugrul 2002 {published data only}
Weisman 1992 {published data only}
-
- Weisman LE, Stoll BJ, Kueser TJ, Rubio TT, Frank CG, Heiman HS, et al. Intravenous immune globulin therapy for early onset sepsis in premature neonates. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;121:434‐43. [PUBMED: 1517923 ] - PubMed
Werdan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Werdan K, Pilz G, Bujdoso O, Frauberger P, Neeser G, Schmeider RE, et al. Score‐based immunoglobulin G therapy of patients with sepsis: The SBITS study. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35:2693‐701. [PUBMED: 18074471] - PubMed
Wesoly 1990 {published data only}
-
- Wesoly C, Kipping N, Grundmann R. Immunoglobulin therapy of postoperative sepsis [Immunglobulintherapie der postoperativen Sepsis]. Zeitschrift für experimentelle Chirurgie, Transplantation, und künstliche Organe: Organ der Sektion Experimentelle Chirurgie der Gesellschaft für Chirurgie der DDR 1990;23:213‐6. [CENTRAL: CN‐00075746; PUBMED: 2095647] - PubMed
Yakut 1998 {published data only}
-
- Yakut M, Cetiner S, Akin A, Tan A, Kaymakcioglu N, Simsek A, et al. Effects of immunoglobulin G on surgical sepsis and septic shock [Sepsisdeki hastalarda immunoglobulin G (IGG) kulianiminin mortalite oranina etkisi]. Bulletin of Gulhane Military Medical Academy 1998;40:76‐81. [CENTRAL: CN‐00200598]
Ziegler 1991 {published data only}
-
- Ziegler EJ, Fisher CJ, Sprung CL, Straube RC, Sadoff JC, Foulke GE, et al. Treatment of gram‐negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA‐1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. The HA‐1A Sepsis Study Group.l. The New England Journal of Medicine 1991;324:429‐36. [PUBMED: 1988827] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aitchison 1985 {published data only}
-
- Aitchison JM, Arbuckle DD. Anti‐endotoxin in the treatment of surgical septic shock. Results of a randomized double‐blind trial. South African Medical Journal 1985;68:787‐9. [PUBMED: 3906941 ] - PubMed
Bojic 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bojic I, Begovic V, Trnjak Z, Dokik M. The significance of immunoglobulins in the treatment of patients with sepsis and septic shock. Vojnosanitetski Pregled. Military‐medical and Pharmaceutical Review 1998;55 (2 Suppl):75‐8. [PUBMED: 9623363 ] - PubMed
Cairo 1992 {published data only}
-
- Cairo MS, Worcester CC, Rucker RW, Hanten S, Amlie RN, Sender L, et al. Randomized trial of granulocyte transfusions versus intravenous immune globulin therapy for neonatal neutropenia and sepsis. Journal of Pediatrics 1992;120:281‐5. [PUBMED: 1735830 ] - PubMed
Calandra 1988 {published data only}
-
- Calandra T, Glauser MP, Schellekens J, Verhoef J. Treatment of gram‐negative septic shock with human IgG antibody to Escherichia coli J5: a prospective double‐blind, randomized trial. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988;158:312‐9. [PUBMED: 3136210] - PubMed
Christensen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Christensen RD, Brown MS, Hall DC, Lassiter HA, Hill HR. Effect on neutrophil kinetics and serum opsonic capacity of intravenous administration of immune globulin to neonates with clinical signs of early‐onset sepsis. The Journal of Pediatrics 1991;118:606‐14. [PUBMED: 1901083] - PubMed
De Groote 1989 {published data only}
-
- Groote MA, Martin MA, Densen P, Pfaller MA, Wenzel RP. Plasma tumor necrosis factor levels in patients with presumed sepsis. Results in those treated with antilipid A antibody vs. placebo. JAMA 1989;262:249‐51. [PUBMED: 2739019] - PubMed
Dominioni 1991 {published data only}
-
- Dominioni L, Dionigi R, Zanello M, Chiaranda M, Dionigi R, Acquarolo A, et al. Effects of high‐dose IgG on survival of surgical patients with sepsis scores of 20 or greater. Archives of Surgery 1991;126:236‐40. [PUBMED: 1992998] - PubMed
El Nawawy 2005 {published data only}
-
- El‐Nawawy A, El‐Kinany H, Hamdy El‐Sayed M, Boshra N. Intravenous polyclonal immunoglobulin administration to sepsis syndrome patients: a prospective study in a pediatric intensive care unit. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 2005;51:271‐8. [PUBMED: 15917261 ] - PubMed
Fischer 1983 {published data only}
-
- Fischer GW, Hunter KW, Hemming VG, Wilson SR. Functional antibacterial activity of a human intravenous immunoglobulin preparation: in vitro and in vivo studies. Vox Sanguinis 1983;44:296‐9. [PUBMED: 6344430] - PubMed
Fisher 1993 {published data only}
-
- Fisher CJ Jr, Opal SM, Dhainaut JF, Stephens S, Zimmerman JL, Nightingale P, et al. Influence of an anti‐tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibody on cytokine levels in patients with sepsis. The CB0006 Sepsis Syndrome Study Group. Critical Care Medicine 1993;21:318‐27. [PUBMED: 8440099 ] - PubMed
Fisher 1996 {published data only}
-
- Fisher CJ, Agosti JM, Opal SM, Lowry SF, Balk RA, Sadoff JC, et al. Treatment of septic shock with the tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein. The Soluble TNF Receptor Sepsis Study Group. The New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334:1697‐702. [CENTRAL: CN‐00125377; PUBMED: 8637514] - PubMed
Freeman 1999 {published data only}
-
- Freeman BD, Eichacker PQ, Natanson C. The role of inflammation in sepsis and septic shock: a meta‐analysis of both clinical and pre‐clinical trials of anti‐inflammatory therapies. In: Gallin JI, Snyderman R editor(s). Inflammation: Basic Principles and Clinical Correlates. 3rd Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Williams, 1999:965‐76.
Gokalp 1994 {published data only}
-
- Gökalp AS, Toksoy HB, Türkay S, Bakici MZ, Kaya R. Intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of Salmonella typhimurium infections in preterm neonates. Clinical Pediatrics 1994;33:349‐52. [PUBMED: 8200169 ] - PubMed
Gunes 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gunes T, Koklu E, Buyukkayhan D, Kurtoglu S, Karakukcu M, Patiroglu T. Exchange transfusion or intravenous immunoglobulin therapy as an adjunct to antibiotics for neonatal sepsis in developing countries: a pilot study. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2006;26:39‐42. [PUBMED: 16494703 ] - PubMed
Haque 1995 {published data only}
Homan 1990 {published data only}
-
- Homan SE, Hall RT, Hall SL, Meade VM, Kurth CG. Safety of intravenous immunoglobulin in neonates at risk for sepsis. American Journal of Perinatology 1990;7:267‐72. [PUBMED: 2121151] - PubMed
Jaspers 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jaspers L, Marget W, Mar PJ, Hoffmann K, Langecker P, Ruckdeschel G, et al. Antibody to lipid A in the treatment of septic shock. Infection 1987;15 Suppl 2:89‐95. [PUBMED: 3301683] - PubMed
Jenson 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jenson HB, Pollock BH. Meta‐analyses of intravenous immune globulin for prevention and treatment of neonatal sepsis. Pediatrics 1997;99(2):E2. [PUBMED: 9099759 ] - PubMed
Jesdinsky 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jesdinsky HJ, Tempel G, Castrup HJ, Seifert J. Cooperative group of additional immunoglobulin therapy in severe bacterial infections: results of a multicenter randomized controlled trial in cases of diffuse fibrinopurulent peritonitis. Klinische Wochenschrift 1987;65:1132‐8. [PUBMED: 3323648] - PubMed
Jones 1995 {published data only}
-
- Jones EB. Prophylactic anti‐lipopolysaccharide freeze‐dried plasma in major burns: a double blind controlled trial. Burns 1995;21:267‐72. [PUBMED: 7662126] - PubMed
Kaul 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kaul R, McGeer A, Norrby‐Teglund A, Kotb M, Schwartz B, O'Rourke K, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for streptococcal toxic shock syndrome‐‐a comparative observational study. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1999;28:800‐7. [PUBMED: 10825042] - PubMed
Kay 1996 {unpublished data only}
-
- Kay CA. Can better measures of cytokine responses be obtained to guide cytokine inhibition?. Knoll AG, Ludwigshafen, Germany. Presentation and handout. Cambridge Health Institutes' Designing Better Drugs and Trials for Sepsis/SIRS: Reducing mortality to patients and suppliers. Washington, DC, February 20‐21, 1996.
Kett 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kett DH, Quartin AA, Sprung CL, Fisher CJ Jr, Peña MA, Heard SO, et al. An evaluation of the hemodynamic effects of HA‐1A human monoclonal antibody. Critical Care Medicine 1994;22:1227‐34. [PUBMED: 8045141] - PubMed
Kornelisse 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kornelisse RF, Hazelzet JA, Hop WC, Spanjaard L, Suur MH, Voort E, et al. Meningococcal septic shock in children: clinical and laboratory features, outcome and development of a prognostic score. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1997;25:640‐6. [PUBMED: 9314453 ] - PubMed
Kreymann 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kreymann KG, Heer G, Nierhaus A, Kluge S. Use of polyclonal immunoglobulins as adjunctive therapy for sepsis or septic shock. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35:2677‐85. [PUBMED: 18074464] - PubMed
Lacy 1995 {published data only}
Laupland 2007 {published data only}
-
- Laupland KB, Kirkpatrick AW, Delaney A. Polyclonal intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock in critically ill adults: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Critical Care Medicine 2007;35:2686‐92. [PUBMED: 18074465 ] - PubMed
Marenovic 1998 {published data only}
-
- Marenovic T, Filipovic D, Lukic Z, Dokic G. High doses of immunoglobulins decrease mortality rate of surgical patients with severe intraabdominal infections and sepsis. Vojnosanitetski Pregled. Military‐medical and Pharmaceutical Review 1998;55 (2 Suppl):71‐4. [PUBMED: 9623362 ] - PubMed
Okimoto 1985 {published data only}
-
- Okamoto Y, Maehara K, Mase K, Iida Y, Yasunaga K, Okubo H, et al. Clinical studies on the effectiveness of SM‐4300, a new non‐modified gamma globulin preparation suitable for intravenous use, in refractory infections. The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics 1985;38:2515‐25. [PUBMED: 4079018] - PubMed
Panko 1976 {published data only}
-
- Panko GF. Use of staphylococcal plasma and antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin in treatment of staphylococcal sepsis. Khirurgiia 1976;9:95‐8. [PUBMED: 979012 ] - PubMed
Pilz 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pilz G, Appel R, Kreuzer E, Werdan K. Comparison of early IgM‐enriched immunoglobulin vs. polyvalent IgG administration in score‐identified postcardiac surgical patients at high risk for sepsis. Chest 1997;111:419‐26. [PUBMED: 9041991] - PubMed
Pittet 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pittet D, Harbarth S, Suter PM, Reinhart K, Leighton K, Barker C, et al. Impact of immunomodulating therapy on morbidity in patients with severe sepsis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1999;160:852‐7. [PUBMED: 10471608] - PubMed
Schedel 1996 {published data only}
-
- Schedel I, Dreichhausen U. [Therapy of gram‐negative septicotoxic diseases with pentaglobin ‐ immunoglobulin with increased IgM content: a prospective randomized clinical study]. Anesteziologiia i Reanimatologiia 1996;199:4‐9. [CENTRAL: CN‐00129822; PUBMED: 8967617] - PubMed
Sidiropolous 1981 {published data only}
-
- Sidiropolous D, Bohme U, Muralt G, Morell A, Barandun S. Immunoglobulin substitution in the treatment of neonatal septicemia. Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift 1981;111:1649‐55. [PUBMED: 7302548] - PubMed
Sidiropoulos 1986 {published data only}
-
- Sidiropoulos D, Boehme U, Muralt G, Morell A, Barandun S. Immunoglobulin supplementation in prevention or treatment of neonatal sepsis. Pediatric Infectious Disease 1986;5:S193‐94. [PUBMED: 3714523] - PubMed
Tomii 1985 {published data only}
-
- Tomii M, Kobayashi Y, Fujimori I. Clinical study of SM‐4300 in the field of medicine. The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics 1985;38:2503‐8. [PUBMED: 3935825] - PubMed
Turgeon 2007 {published data only}
-
- Turgeon AF, Hutton B, Fergusson DA, McIntyre L, Tinmouth AA, Cameron DW, et al. Meta‐analysis: intravenous immunoglobulin in critically ill adult patients with sepsis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2007;146:193‐203. [PUBMED: 17283351 ] - PubMed
Ueda 1985 {published data only}
-
- Ueda T, Fujimoto M, Sakai K, Sasaki T, Morimoto Y, Mitsuyoshi H, et al. A clinical trial of SM‐4300 against severe infections in surgery. The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics 1985;38:2647‐59. [PUBMED: 3908740] - PubMed
Wang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wang Y, Dou L, Zhang H, Zhao B, Wang D, Cao S. Treatment of septic thrombocytopenia with immunoglobulin. Chinese Journal of Emergency Medicine 2006;15:905‐8. [CENTRAL: CN‐00613262; EMBASE: 2006513788]
Werdan 1996 {published data only}
-
- Werdan K, Pilz G. Supplemental immune globulins in sepsis: a critical appraisal. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 1996;104 Suppl 1:83‐90. [PUBMED: 8625550] - PubMed
Wortel 1992 {published data only}
-
- Wortel CH, Möhlen MA, Deventer SJ, Sprung CL, Jastremski M, Lubbers MJ, et al. Effectiveness of a human monoclonal anti‐endotoxin antibody (HA‐1A) in gram‐negative sepsis: relationship to endotoxin and cytokine levels. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 1992;166:1367‐74. [PUBMED: 1431255] - PubMed
Yavuz 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yavuz L, Aynali G, Aynali A, Alacala A, Kutuk S, Ceylan BG. The effects of adjuvant immunoglobulin M‐enriched immunoglobulin therapy on mortality rate and renal function in sepsis‐induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome: retrospective analysis of intensive care unit patients. The Journal of International Medical Research 2012;40:1166‐74. - PubMed
Zeni 1997 {published data only}
-
- Zeni F, Freeman BD, Natanson C. Anti‐inflammatory therapies to treat sepsis and septic shock: a reassessment. Critical Care Medicine 1997;25:1095‐100. [PUBMED: 9233726 ] - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Yildizdas 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yildizidas D, Yapicioglu H, Tumgor G, Erbey F. Does polyclonal intravenous immunoglobulin reduce mortality in septic children in pediatric intensive care unit? [Cocuk yogun bakim unitesi'nde sepsis nedeni ile izlenen hastalarda poliklonal intravenoz immunglobulin tedavisi mortaliteyi azaltiyor mu?]. Cocuk Sagligi Ve Hastaliklari Dergisi 2005;48:136‐41. [CENTRAL: CN‐00569372; EMBASE: 2005248022]
Additional references
Abraham 1994
-
- Abraham E, Raffin TA. Sepsis therapy trials ‐ continued disappointment or reason for hope?. JAMA 1994;271:1876‐78. [PUBMED: 8196148 ] - PubMed
Alejandria 2000
-
- Alejandria MM, Lansang MA, Fonbuena GE, Fadreguilan E, Timbreza F, Luna M, et al. Epidemiology and predictors of mortality from sepsis in medical patients at UP‐PGH. Philippine Journal of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 2000;29:23‐32.
Annane 2009
-
- Annane D. Improving clinical trials in the critically ill: unique challenge ‐sepsis. Critical Care Medicine 2009;37 Suppl 1:117‐28. - PubMed
Bone 1991
-
- Bone RC. A critical evaluation of new agents for the treatment of sepsis. JAMA 1991;266:1686‐90. [PUBMED: 1886193 ] - PubMed
Bone 1992
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis: The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. Chest 1992;101:1644‐55. - PubMed
Cappelleri 1995
-
- Cappelleri JC, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH, Ferranti SD, Aubert M, Chalmers TC, et al. Large trials vs meta‐analysis of smaller trials ‐ how do their results compare?. JAMA 1999;276:1332‐8. [PUBMED: 8861993] - PubMed
Dahlberg 1997
-
- Dahlberg PS, David DL. Endotoxins and sepsis. In: Fein AM, Abrahan EM, et al. editor(s). Sepsis and multiorgan failure. USA: Williams & Wilkins, 1997:45‐61.
Dellinger 2008
Dellinger 2013
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal S, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2012. Critical Care Medicine 2013;41:580‐637. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, [updated March 2011].
Levy 2003
-
- Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, et al. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International sepsis definitions conference. Critical Care Medicine 2003;31:1250‐6. - PubMed
Norrby‐Teglund 2003
-
- Norrby‐Teglund A, Ihendyane N, Darenberg J. Intravenous immunoglobulin adjunctive therapy in sepsis, with special emphasis on severe invasive group A streptococcal infections. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2003;35:683‐9. [PUBMED: 14620155] - PubMed
Nydegger 1997
-
- Nydegger UE. Sepsis and polyspecific intravenous immunoglobulins. Journal of Clinical Apheresis 1997;12:93‐9. [PUBMED: 9263117 ] - PubMed
Nydegger 1999
-
- Nydegger UE, Sturzenegger M. Adverse effects of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Drug Safety 1999;21:171‐85. - PubMed
Ohlsson 2013
Phua 2011
Pildal 2004
-
- Pildal J, Gøtzsche PC. Polyclonal immunoglobulin for treatment of bacterial sepsis: a systematic review. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2004;39:38‐46. [PUBMED: 15206051] - PubMed
Rangel‐Frausto 1995
-
- Rangel‐Frausto MS, Pittet D, Costigan M, Hwang T, Davis CS, Wenzel RP. The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). JAMA 1995;274:968‐74. [PUBMED: 7799491 ] - PubMed
RevMan 5.2 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Rivers 2001
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early Goal‐Directed Therapy Collaborative Group. Early goal‐directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. The New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345:1368‐77. [PUBMED: 1794169 ] - PubMed
Sibbald 1995
-
- Sibbald WJ, Vincent JL. Round table conference on clinical trials for the treatment of sepsis. Critical Care Medicine 1995;23:394‐9. [PUBMED: 7867364] - PubMed
Soares 2012
-
- Soares MO, Welton NJ, Harrison DA, Peura P, Shankar‐Hari M, Harvey SE, et al. An evaluation of the feasibility, cost and value of information of a multicentre randomised controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin for sepsis (severe sepsis and septic shock): incorporating a systematic review,meta‐analysis and value of information analysis. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(7):1‐186. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Sundararajan 2006
Taguiang‐Abu 2008
-
- Taguiang‐Abu CU, Alejandria MM. Clinical determinants of outcome of severe sepsis among adult patients at the Philippine General Hospital Intensive Care Units. Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine 2008;46:103‐12.
Tanriover 2006
Villa 1995
-
- Villa L, Baleva E, Tiu D, Coronel R. Sepsis profile among patients in a tertiary care hospital. St Luke's Medical Journal 1995;2:45‐9.
Villar 1995
-
- Villar J, Carroli G, Belizan JM. Predictive ability of meta‐analyses of randomized controlled trials. Lancet 1995;345:772‐6. [PUBMED: 7891492 ] - PubMed
Werdan 1997
-
- Werdan K, Pilz G, the SBITs Study Group. Polyvalent immune globulins [Abstract 18]. Shock 1997; Vol. 7 Suppl 5:1918.
Werdan 2001
-
- Werdan K. Pathophysiology of septic shock and multiorgan dysfunction syndrome and various therapeutic approaches with special emphasis on immunoglobulins. Therapeutic Apheresis 2001;5:115‐22. [PUBMED: 11354295] - PubMed
Wortel 1993
-
- Wortel CH. Treatment of gram‐negative septic shock with an immunoglobulin preparation: a prospective randomized clinical trial (Letter to the Editor). Critical Care Medicine 1993;21:163‐5. [PUBMED: 8420724] - PubMed
Zabala 1999
-
- Zabala MLB, Dans LF. Prescribing patterns for immunoglobulin use among pediatricians in 3 Metro Manila hospitals. Conference Proceedings 2nd World Congress of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 1999 Nov 2‐6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

