Regulation of acrAB expression by cellular metabolites in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 24043404
- PMCID: PMC3886929
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkt352
Regulation of acrAB expression by cellular metabolites in Escherichia coli
Abstract
Objectives: Multidrug efflux pumps mediate resistance to antibiotics and other toxic compounds. We studied the role of AcrAB-TolC, the main efflux pump in Escherichia coli, in regulating gene expression.
Methods: Deletion mutants, an acrABp-lacZ fusion and reverse transcription-real-time quantitative PCR experiments were used to study the role of AcrAB-TolC and metabolism in regulating gene expression of the acrAB operon and its transcriptional regulators.
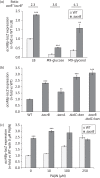
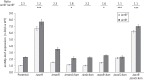
Results: Deletion of the acrB gene increased the expression of the acrAB operon. A similar induction of acrAB was found when acrA or tolC was deleted, and when the pump function was inhibited using phenylalanine-arginine-β-naphthylamide. The induction of acrAB in the ΔacrB strain was totally (AcrR or SoxS) or partially (SoxR or MarA) prevented when the genes for these acrAB regulators were also deleted. The expression of soxS and marA, but not of acrR, was increased in the ΔacrB strain, which also showed altered expression of many other genes related to different cellular processes, including motility. Deletion of the metabolic genes entA and entE (enterobactin biosysnthesis), glpX (gluconeogenesis), cysH (cysteine biosynthesis) and purA (purine biosynthesis) also prevented activation of the acrAB promoter in the ΔacrB strain. Addition of the enterobactin biosynthesis intermediate metabolite 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate induced the expression of acrAB.
Conclusions: These results together suggest a model in which the AcrAB-TolC pump effluxes cellular metabolites that are toxic and/or have a signalling role. If the pump is inactivated or inhibited, these metabolites would accumulate, inactivating AcrR and/or up-regulating soxS and marA expression, ultimately triggering the up-regulation of acrAB expression to restore homeostasis.
Keywords: AcrAB-TolC; acrR; gene regulation; marA; multidrug efflux; soxS.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Improving the organic solvent tolerance of Escherichia coli with vanillin, and the involvement of an AcrAB-TolC efflux pump in vanillin tolerance.J Biosci Bioeng. 2022 Apr;133(4):347-352. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2021.12.015. Epub 2022 Jan 19. J Biosci Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 35063375
-
The Multidrug Efflux Regulator AcrR of Escherichia coli Responds to Exogenous and Endogenous Ligands To Regulate Efflux and Detoxification.mSphere. 2022 Dec 21;7(6):e0047422. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00474-22. Epub 2022 Nov 23. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 36416552 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated Expression of acrAB-tolC and Eight Other Functional Efflux Pumps Through Activating ramA and marA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Microb Drug Resist. 2018 Mar;24(2):120-125. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2017.0086. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Microb Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 28650690
-
Regulation of the AcrAB efflux system by the quorum-sensing regulator AnoR in Acinetobacter nosocomialis.J Microbiol. 2020 Jun;58(6):507-518. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0185-2. Epub 2020 May 27. J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32462488 Review.
-
Improvement of organic solvent tolerance level of Escherichia coli by overexpression of stress-responsive genes.Extremophiles. 1998 Aug;2(3):239-48. doi: 10.1007/s007920050066. Extremophiles. 1998. PMID: 9783171 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure, Assembly, and Function of Tripartite Efflux and Type 1 Secretion Systems in Gram-Negative Bacteria.Chem Rev. 2021 May 12;121(9):5479-5596. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00055. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33909410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide analysis of genes involved in efflux function and regulation within Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Microbiology (Reading). 2023 Feb;169(2):001296. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001296. Microbiology (Reading). 2023. PMID: 36745554 Free PMC article.
-
The induced and intrinsic resistance of Escherichia coli to sanguinarine is mediated by AcrB efflux pump.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0323723. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03237-23. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38038452 Free PMC article.
-
Functional annotation of rhizospheric phageome of the wild plant species Moringa oleifera.Front Microbiol. 2023 May 16;14:1166148. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1166148. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37260683 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Binding and Sensor Specificity of FarR, a Novel TetR Family Regulator Required for Induction of the Fatty Acid Efflux Pump FarE in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jan 11;201(3):e00602-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00602-18. Print 2019 Feb 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30455282 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

