Feedback inhibition of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves mediated by trehalose 6-phosphate
- PMID: 24043444
- PMCID: PMC3813640
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.226787
Feedback inhibition of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves mediated by trehalose 6-phosphate
Abstract
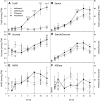
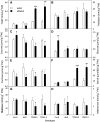
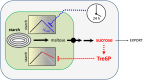
Many plants accumulate substantial starch reserves in their leaves during the day and remobilize them at night to provide carbon and energy for maintenance and growth. In this paper, we explore the role of a sugar-signaling metabolite, trehalose-6-phosphate (Tre6P), in regulating the accumulation and turnover of transitory starch in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) leaves. Ethanol-induced overexpression of trehalose-phosphate synthase during the day increased Tre6P levels up to 11-fold. There was a transient increase in the rate of starch accumulation in the middle of the day, but this was not linked to reductive activation of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. A 2- to 3-fold increase in Tre6P during the night led to significant inhibition of starch degradation. Maltose and maltotriose did not accumulate, suggesting that Tre6P affects an early step in the pathway of starch degradation in the chloroplasts. Starch granules isolated from induced plants had a higher orthophosphate content than granules from noninduced control plants, consistent either with disruption of the phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle that is essential for efficient starch breakdown or with inhibition of starch hydrolysis by β-amylase. Nonaqueous fractionation of leaves showed that Tre6P is predominantly located in the cytosol, with estimated in vivo Tre6P concentrations of 4 to 7 µm in the cytosol, 0.2 to 0.5 µm in the chloroplasts, and 0.05 µm in the vacuole. It is proposed that Tre6P is a component in a signaling pathway that mediates the feedback regulation of starch breakdown by sucrose, potentially linking starch turnover to demand for sucrose by growing sink organs at night.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Tale of Two Sugars: Trehalose 6-Phosphate and Sucrose.Plant Physiol. 2016 Sep;172(1):7-27. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00417. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27482078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sugar-induced increases in trehalose 6-phosphate are correlated with redox activation of ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase and higher rates of starch synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana.Biochem J. 2006 Jul 1;397(1):139-48. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060083. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16551270 Free PMC article.
-
Trehalose 6-phosphate regulates starch synthesis via posttranslational redox activation of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 2;102(31):11118-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503410102. Epub 2005 Jul 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16046541 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and indirect responses of the Arabidopsis transcriptome to an induced increase in trehalose 6-phosphate.Plant Physiol. 2024 Sep 2;196(1):409-431. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae196. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38593032 Free PMC article.
-
Trehalose metabolism in plants.Plant J. 2014 Aug;79(4):544-67. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12509. Epub 2014 May 21. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24645920 Review.
Cited by
-
BABA and Phytophthora nicotianae Induce Resistance to Phytophthora capsici in Chile Pepper (Capsicum annuum).PLoS One. 2015 May 28;10(5):e0128327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128327. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26020237 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics reveals mechanisms of total resistance to extreme illumination of a desert alga.Nat Plants. 2020 Aug;6(8):1031-1043. doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0729-9. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Nat Plants. 2020. PMID: 32719473
-
Management of plant central metabolism by SnRK1 protein kinases.J Exp Bot. 2022 Nov 15;73(20):7068-7082. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac261. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35708960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The redox-sensitive chloroplast trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase AtTPPD regulates salt stress tolerance.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Sep 20;21(9):1289-304. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5693. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24800789 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor Arabidopsis Activating Factor1 Integrates Carbon Starvation Responses with Trehalose Metabolism.Plant Physiol. 2015 Sep;169(1):379-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00917. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26149570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arrivault S, Guenther M, Ivakov A, Feil R, Vosloh D, van Dongen JT, Sulpice R, Stitt M. (2009) Use of reverse-phase liquid chromatography, linked to tandem mass spectrometry, to profile the Calvin cycle and other metabolic intermediates in Arabidopsis rosettes at different carbon dioxide concentrations. Plant J 59: 826–839 - PubMed
-
- Ballicora MA, Frueauf JB, Fu Y, Schürmann P, Preiss J. (2000) Activation of the potato tuber ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase by thioredoxin. J Biol Chem 275: 1315–1320 - PubMed
-
- Baunsgaard L, Lütken H, Mikkelsen R, Glaring MA, Pham TT, Blennow A. (2005) A novel isoform of glucan, water dikinase phosphorylates pre-phosphorylated α-glucans and is involved in starch degradation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 41: 595–605 - PubMed
-
- Blázquez MA, Santos E, Flores CL, Martínez-Zapater JM, Salinas J, Gancedo C. (1998) Isolation and molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis TPS1 gene, encoding trehalose-6-phosphate synthase. Plant J 13: 685–689 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

