Feedback inhibition of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves mediated by trehalose 6-phosphate
- PMID: 24043444
- PMCID: PMC3813640
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.113.226787
Feedback inhibition of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves mediated by trehalose 6-phosphate
Abstract
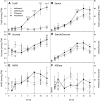
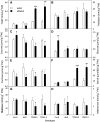
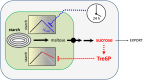
Many plants accumulate substantial starch reserves in their leaves during the day and remobilize them at night to provide carbon and energy for maintenance and growth. In this paper, we explore the role of a sugar-signaling metabolite, trehalose-6-phosphate (Tre6P), in regulating the accumulation and turnover of transitory starch in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) leaves. Ethanol-induced overexpression of trehalose-phosphate synthase during the day increased Tre6P levels up to 11-fold. There was a transient increase in the rate of starch accumulation in the middle of the day, but this was not linked to reductive activation of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. A 2- to 3-fold increase in Tre6P during the night led to significant inhibition of starch degradation. Maltose and maltotriose did not accumulate, suggesting that Tre6P affects an early step in the pathway of starch degradation in the chloroplasts. Starch granules isolated from induced plants had a higher orthophosphate content than granules from noninduced control plants, consistent either with disruption of the phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle that is essential for efficient starch breakdown or with inhibition of starch hydrolysis by β-amylase. Nonaqueous fractionation of leaves showed that Tre6P is predominantly located in the cytosol, with estimated in vivo Tre6P concentrations of 4 to 7 µm in the cytosol, 0.2 to 0.5 µm in the chloroplasts, and 0.05 µm in the vacuole. It is proposed that Tre6P is a component in a signaling pathway that mediates the feedback regulation of starch breakdown by sucrose, potentially linking starch turnover to demand for sucrose by growing sink organs at night.
Figures



References
-
- Arrivault S, Guenther M, Ivakov A, Feil R, Vosloh D, van Dongen JT, Sulpice R, Stitt M. (2009) Use of reverse-phase liquid chromatography, linked to tandem mass spectrometry, to profile the Calvin cycle and other metabolic intermediates in Arabidopsis rosettes at different carbon dioxide concentrations. Plant J 59: 826–839 - PubMed
-
- Ballicora MA, Frueauf JB, Fu Y, Schürmann P, Preiss J. (2000) Activation of the potato tuber ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase by thioredoxin. J Biol Chem 275: 1315–1320 - PubMed
-
- Baunsgaard L, Lütken H, Mikkelsen R, Glaring MA, Pham TT, Blennow A. (2005) A novel isoform of glucan, water dikinase phosphorylates pre-phosphorylated α-glucans and is involved in starch degradation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 41: 595–605 - PubMed
-
- Blázquez MA, Santos E, Flores CL, Martínez-Zapater JM, Salinas J, Gancedo C. (1998) Isolation and molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis TPS1 gene, encoding trehalose-6-phosphate synthase. Plant J 13: 685–689 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

