C-terminal processing of reaction center protein D1 is essential for the function and assembly of photosystem II in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 24043802
- PMCID: PMC3791762
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1313894110
C-terminal processing of reaction center protein D1 is essential for the function and assembly of photosystem II in Arabidopsis
Abstract
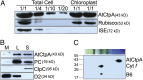
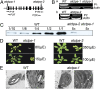
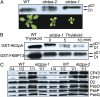
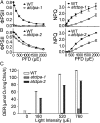
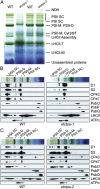
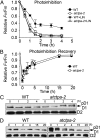
Photosystem II (PSII) reaction center protein D1 is synthesized as a precursor (pD1) with a short C-terminal extension. The pD1 is processed to mature D1 by carboxyl-terminal peptidase A to remove the C-terminal extension and form active protein. Here we report functional characterization of the Arabidopsis gene encoding D1 C-terminal processing enzyme (AtCtpA) in the chloroplast thylakoid lumen. Recombinant AtCtpA converted pD1 to mature D1 and a mutant lacking AtCtpA retained all D1 in precursor form, confirming that AtCtpA is solely responsible for processing. As with cyanobacterial ctpa, a knockout Arabidopsis atctpa mutant was lethal under normal growth conditions but was viable with sucrose under low-light conditions. Viable plants, however, showed deficiencies in PSII and thylakoid stacking. Surprisingly, unlike its cyanobacterial counterpart, the Arabidopsis mutant retained both monomer and dimer forms of the PSII complexes that, although nonfunctional, contained both the core and extrinsic subunits. This mutant was also essentially devoid of PSII supercomplexes, providing an unexpected link between D1 maturation and supercomplex assembly. A knock-down mutant expressing about 2% wild-type level of AtCtpA showed normal growth under low light but was stunted and accumulated pD1 under high light, indicative of delayed C-terminal processing. Although demonstrating the functional significance of C-terminal D1 processing in PSII biogenesis, our study reveals an unsuspected link between D1 maturation and PSII supercomplex assembly in land plants, opening an avenue for exploring the mechanism for the association of light-harvesting complexes with the PSII core complexes.
Keywords: photoinhibition; photosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of mature D1 leads to compromised CP43 assembly in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Feb 20;21(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02888-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33610179 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis thylakoid protein PAM68 is required for efficient D1 biogenesis and photosystem II assembly.Plant Cell. 2010 Oct;22(10):3439-60. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.077453. Epub 2010 Oct 5. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20923938 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxyl-terminal processing of the D1 protein and photoactivation of water-splitting in photosystem II. Partial purification and characterization of the processing enzyme from Scenedesmus obliquus and Pisum sativum.J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5424-33. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1544920
-
Processing of D1 Protein: A Mysterious Process Carried Out in Thylakoid Lumen.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 25;23(5):2520. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052520. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of photosystem II: a proteomic approach to thylakoid protein complexes.J Exp Bot. 2005 Jan;56(411):347-56. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri041. Epub 2004 Nov 29. J Exp Bot. 2005. PMID: 15569703 Review.
Cited by
-
Rubredoxin 1 Is Required for Formation of the Functional Photosystem II Core Complex in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 23;13:824358. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.824358. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35283894 Free PMC article.
-
A Proteolytic Complex Targets Multiple Cell Wall Hydrolases in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mBio. 2018 Jul 17;9(4):e00972-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00972-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30018106 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive responses of plants to light stress: mechanisms of photoprotection and acclimation. A review.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Mar 28;16:1550125. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1550125. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40225024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primary and Higher Order Structure of the Reaction Center from the Purple Phototrophic Bacterium Blastochloris viridis: A Test for Native Mass Spectrometry.J Proteome Res. 2018 Apr 6;17(4):1615-1623. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00897. Epub 2018 Mar 2. J Proteome Res. 2018. PMID: 29466012 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminus of substrates is critical but not sufficient for their degradation by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa CtpA protease.J Bacteriol. 2020 Jun 1;202(16):e00174-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00174-20. Online ahead of print. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32482720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferreira KN, Iverson TM, Maghlaoui K, Barber J, Iwata S. Architecture of the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving center. Science. 2004;303(5665):1831–1838. - PubMed
-
- Guskov A, et al. Cyanobacterial photosystem II at 2.9-A resolution and the role of quinones, lipids, channels and chloride. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16(3):334–342. - PubMed
-
- Adir N, Zer H, Shochat S, Ohad I. Photoinhibition - a historical perspective. Photosynth Res. 2003;76(1-3):343–370. - PubMed
-
- Satoh K, Yamamoto Y. The carboxyl-terminal processing of precursor D1 protein of the photosystem II reaction center. Photosynth Res. 2007;94(2-3):203–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

