Comparative efficacy of aclidinium versus glycopyrronium and tiotropium, as maintenance treatment of moderate to severe COPD patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 24043936
- PMCID: PMC3772873
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S48967
Comparative efficacy of aclidinium versus glycopyrronium and tiotropium, as maintenance treatment of moderate to severe COPD patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Aclidinium bromide is a new long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA) indicated for maintenance bronchodilator treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The efficacy of aclidinium was compared with tiotropium and glycopyrronium, using a network meta-analysis (NMA) of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in moderate-to-severe COPD patients.
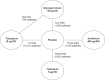
Methods: A systematic review was performed to identify RCTs evaluating aclidinium 400 μg twice daily (BID), glycopyrronium 50 μg once daily (OD), tiotropium 18 μg OD, or tiotropium 5 μg OD in adults with moderate-to-severe COPD. The outcomes of interest were: trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1); St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score and proportion of patients achieving ≥4 unit change; Transition Dyspnea Index (TDI) focal score and proportion of patients achieving ≥1 point change. The results were synthesized by means of a Bayesian NMA.
Results: Twenty-one studies (22,542 patients) were included: aclidinium 400 μg BID (three studies); tiotropium 5 μg OD (three studies); tiotropium 18 μg OD (13 studies); and glycopyrronium 50 μg OD (two studies). Regarding trough FEV1 at 24 weeks, aclidinium demonstrated comparable efficacy to tiotropium 5 μg (difference in change from baseline [CFB]), (0.02 L [95% credible interval CrI -0.05, 0.09]); tiotropium 18 μg (0.02 L [95% CrI -0.05, 0.08]); and glycopyrronium (0.00 L [95% CrI -0.07, 0.07]). Aclidinium resulted in higher improvement in SGRQ score at 24 weeks, compared to tiotropium 5 μg (difference in CFB, -2.44 [95% CrI -4.82, -0.05]); and comparable results to tiotropium 18 μg (-1.80 [95% CrI -4.52, 0.14]) and glycopyrronium (-1.52 [95% CrI -4.08, 1.03]). Improvements in TDI score were comparable for all treatments.
Conclusion: Maintenance treatment with aclidinium 400 μg BID is expected to produce similar improvements in lung function, health-related quality of life, and dyspnea compared to tiotropium 5 μg OD; tiotropium 18 μg OD; and glycopyrronium 50 μg OD.
Keywords: COPD; aclidinium; glycopyrronium; network meta-analysis; systematic review; tiotropium.
Figures


References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung D Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD (GOLD) Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/uploads/users/files/GOLD_Report_2013_Feb20.pdfAccessed February 25, 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults in primary and secondary care (partial update) National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; 2013[updated May 8, 2013] Available from: http://guidance.nice.org.uk/cg101Accessed May 13, 2013
-
- United States Food and Drug Administration Prescribing Information: TUDORZA PRESSAIR Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/202450s000lbl.pdfAccessed February 25, 2013
-
- Boehringer Ingelheim Limited [homepage on the Internet] Summary of product characteristics: Spiriva® Respimat® 2.5 microgram, Solution for Inhalation Boehringer Ingelheim Limited; [updated June 27, 2013. Available from: http://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/20134Accessed July 2, 2013
-
- European Medicines Agency Summary of Product Characteristics: Eklira Genuair 322 micrograms inhalation powder Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info...Accessed February 25, 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

