MicroRNAs: history, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease
- PMID: 24045890
- PMCID: PMC4013251
- DOI: 10.1177/0300985813502820
MicroRNAs: history, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease
Abstract
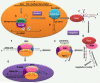
The discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs) in 1993 followed by developments and discoveries in small RNA biology have redefined the biological landscape by significantly altering the longstanding dogmas that defined gene regulation. These small RNAs play a significant role in modulation of an array of physiological and pathological processes ranging from embryonic development to neoplastic progression. Unique miRNA signatures of various inherited, metabolic, infectious, and neoplastic diseases have added a new dimension to the studies that look at their pathogenesis and highlight their potential to be reliable biomarkers. Also, altering miRNA functionality and the development of novel in vivo delivery systems to achieve targeted modulation of specific miRNA function are being actively pursued as novel approaches for therapeutic intervention in many diseases. Here we review the current body of knowledge on the role of miRNAs in development and disease and discuss future implications.
Keywords: animal microRNA; apoptomiR; biomarkers; circulating miRNA; miR; oncomiR.
© The Author(s) 2013.
Figures
References
-
- Antonini D, Russo MT, De Rosa L, et al. Transcriptional repression of miR-34 family contributes to p63-mediated cell cycle progression in epidermal cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:1249–1257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

