Binding of the sialic acid-binding lectin, Siglec-9, to the membrane mucin, MUC1, induces recruitment of β-catenin and subsequent cell growth
- PMID: 24045940
- PMCID: PMC3814777
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.471318
Binding of the sialic acid-binding lectin, Siglec-9, to the membrane mucin, MUC1, induces recruitment of β-catenin and subsequent cell growth
Abstract
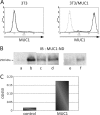
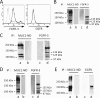
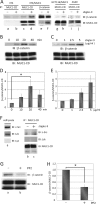
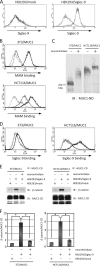
Because MUC1 carries a variety of sialoglycans that are possibly recognized by the siglec family, we examined MUC1-binding siglecs and found that Siglec-9 prominently bound to MUC1. An immunochemical study showed that Siglec-9-positive immune cells were associated with MUC1-positive cells in human colon, pancreas, and breast tumor tissues. We investigated whether or not this interaction has any functional implications for MUC1-expressing cells. When mouse 3T3 fibroblast cells and a human colon cancer cell line, HCT116, stably transfected with MUC1cDNA were ligated with recombinant soluble Siglec-9, β-catenin was recruited to the MUC1 C-terminal domain, which was enhanced on stimulation with soluble Siglec-9 in dose- and time-dependent manners. A co-culture model of MUC1-expressing cells and Siglec-9-expressing cells mimicking the interaction between MUC1-expressing malignant cells, and Siglec-9-expressing immune cells in a tumor microenvironment was designed. Brief co-incubation of Siglec-9-expressing HEK293 cells, but not mock HEK293 cells, with MUC1-expressing cells similarly enhanced the recruitment of β-catenin to the MUC1 C-terminal domain. In addition, treatment of MUC1-expressing cells with neuraminidase almost completely abolished the effect of Siglec-9 on MUC1-mediated signaling. The recruited β-catenin was thereafter transported to the nucleus, leading to cell growth. These findings suggest that Siglec-9 expressed on immune cells may play a role as a potential counterreceptor for MUC1 and that this signaling may be another MUC1-mediated pathway and function in parallel with a growth factor-dependent pathway.
Keywords: Lectin; Mucins; Signaling; Tumor Microenvironment; β-Catenin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The mucin MUC1 modulates the tumor immunological microenvironment through engagement of the lectin Siglec-9.Nat Immunol. 2016 Nov;17(11):1273-1281. doi: 10.1038/ni.3552. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Nat Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27595232 Free PMC article.
-
Engagement of myelomonocytic Siglecs by tumor-associated ligands modulates the innate immune response to cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Sep 30;111(39):14211-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409580111. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25225409 Free PMC article.
-
A soluble form of Siglec-9 provides an antitumor benefit against mammary tumor cells expressing MUC1 in transgenic mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jul 18;450(1):532-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24924635
-
Siglec Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 13;12:790317. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.790317. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34966391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sialoglycans and Siglecs Can Shape the Tumor Immune Microenvironment.Trends Immunol. 2020 Apr;41(4):274-285. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.02.001. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32139317 Review.
Cited by
-
The Paired Siglecs in Brain Tumours Therapy: The Immunomodulatory Effect of Dexamethasone and Temozolomide in Human Glioma In Vitro Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1791. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041791. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670244 Free PMC article.
-
LINC01004-SPI1 axis-activated SIGLEC9 in tumor-associated macrophages induces radioresistance and the formation of immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Jun;72(6):1835-1851. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03364-5. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36688997 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Microenvironment-Associated Extracellular Matrix Components Regulate NK Cell Function.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 29;11:73. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00073. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32063906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABA selectively increases mucin-1 expression in isolated pig jejunum.Genes Nutr. 2015 Nov;10(6):47. doi: 10.1007/s12263-015-0497-8. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Genes Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26471792 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-associated hypersialylated MUC1 drives the differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages with a pathogenic phenotype.Commun Biol. 2020 Nov 4;3(1):644. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01359-5. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 33149188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ligtenberg M. J., Kruijshaar L., Buijs F., van Meijer M., Litvinov S. V., Hilkens J. (1992) Cell-associated episialin is a complex containing two proteins derived from a common precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 6171–6177 - PubMed
-
- Parry S., Silverman H. S., McDermott K., Willis A., Hollingsworth M. A., Harris A. (2001) Identification of MUC1 proteolytic cleavage sites in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 283, 715–720 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

