Agonist-dependent signaling by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors is regulated by association with lipid domains
- PMID: 24045944
- PMCID: PMC3814796
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.475863
Agonist-dependent signaling by group I metabotropic glutamate receptors is regulated by association with lipid domains
Abstract
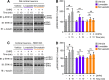
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs), mGluR1 and mGluR5, play critical functions in forms of activity-dependent synaptic plasticity and synapse remodeling in physiological and pathological states. Importantly, in animal models of fragile X syndrome, group I mGluR activity is abnormally enhanced, a dysfunction that may partly underlie cognitive deficits in the condition. Lipid rafts are cholesterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that are thought to form transient signaling platforms for ligand-activated receptors. Many G protein-coupled receptors, including group I mGluRs, are present in lipid rafts, but the mechanisms underlying recruitment to these membrane domains remain incompletely understood. Here, we show that mGluR1 recruitment to lipid rafts is enhanced by agonist binding and is supported at least in part by an intact cholesterol recognition/interaction amino acid consensus (CRAC) motif in the receptor. Substitutions of critical residues in the motif reduce mGluR1 association with lipid rafts and agonist-induced, mGluR1-dependent activation of extracellular-signal-activated kinase1/2 MAP kinase (ERK-MAPK). We find that alteration of membrane cholesterol content or perturbation of lipid rafts regulates agonist-dependent activation of ERK-MAPK by group I mGluRs, suggesting a potential function for cholesterol as a positive allosteric modulator of receptor function(s). Together, these findings suggest that drugs that alter membrane cholesterol levels or directed to the receptor-cholesterol interface could be employed to modulate abnormal group I mGluR activity in neuropsychiatric conditions, including fragile X syndrome.
Keywords: CRAC Motif; Cholesterol; ERK; Glutamate Receptors Metabotropic; Lipid Raft; Protein Motifs.
Figures


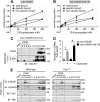
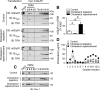
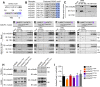
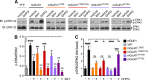

Similar articles
-
Role of Spinophilin in Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Endocytosis, Signaling, and Synaptic Plasticity.J Biol Chem. 2016 Aug 19;291(34):17602-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.722355. Epub 2016 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27358397 Free PMC article.
-
Pyk2 uncouples metabotropic glutamate receptor G protein signaling but facilitates ERK1/2 activation.Mol Brain. 2010 Jan 21;3:4. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-3-4. Mol Brain. 2010. PMID: 20180987 Free PMC article.
-
The post-synaptic scaffolding protein tamalin regulates ligand-mediated trafficking of metabotropic glutamate receptors.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 19;295(25):8575-8588. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011979. Epub 2020 May 6. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32376687 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of membrane/lipid rafts with the cytoskeleton: impact on signaling and function: membrane/lipid rafts, mediators of cytoskeletal arrangement and cell signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1838(2):532-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.07.018. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23899502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors and fragile x mental retardation protein: partners in translational regulation at the synapse.Sci Signal. 2008 Feb 5;1(5):pe6. doi: 10.1126/stke.15pe6. Sci Signal. 2008. PMID: 18272470 Review.
Cited by
-
Statins and the Brain: More than Lipid Lowering Agents?Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019;17(1):59-83. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170703101816. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019. PMID: 28676012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary history of calcium-sensing receptors unveils hyper/hypocalcemia-causing mutations.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Nov 12;20(11):e1012591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012591. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 39531485 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Diversity in Lipid-Protein Interactions.Chem Rev. 2019 May 8;119(9):5775-5848. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00451. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Chem Rev. 2019. PMID: 30758191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spinocerebellar Ataxia 44 Caused by a Novel GRM1 Variant: Reviewing the Contrasting Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Two GRM1-Associated Hereditary Ataxias.Cerebellum. 2025 Apr 9;24(3):84. doi: 10.1007/s12311-025-01837-8. Cerebellum. 2025. PMID: 40199824
-
Contribution of Membrane Lipids to Postsynaptic Protein Organization.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021 Nov 23;13:790773. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2021.790773. eCollection 2021. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34887741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anwyl R. (2009) Metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. Neuropharmacology 56, 735–740 - PubMed
-
- Snyder E. M., Philpot B. D., Huber K. M., Dong X., Fallon J. R., Bear M. F. (2001) Internalization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in response to mGluR activation. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1079–1085 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

