Histoplasmosis after solid organ transplant
- PMID: 24046304
- PMCID: PMC3814825
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cit593
Histoplasmosis after solid organ transplant
Abstract
Background: To improve our understanding of risk factors, management, diagnosis, and outcomes associated with histoplasmosis after solid organ transplant (SOT), we report a large series of histoplasmosis occurring after SOT.
Methods: All cases of histoplasmosis in SOT recipients diagnosed between 1 January 2003 and 31 December 2010 at 24 institutions were identified. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were collected.
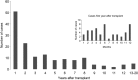
Results: One hundred fifty-two cases were identified: kidney (51%), liver (16%), kidney/pancreas (14%), heart (9%), lung (5%), pancreas (2%), and other (2%). The median time from transplant to diagnosis was 27 months, but 34% were diagnosed in the first year after transplant. Twenty-eight percent of patients had severe disease (requiring intensive care unit admission); 81% had disseminated disease. Urine Histoplasma antigen detection was the most sensitive diagnostic method, positive in 132 of 142 patients (93%). An amphotericin formulation was administered initially to 73% of patients for a median duration of 2 weeks; step-down therapy with an azole was continued for a median duration of 12 months. Ten percent of patients died due to histoplasmosis with 72% of deaths occurring in the first month after diagnosis; older age and severe disease were risk factors for death from histoplasmosis. Relapse occurred in 6% of patients.
Conclusions: Although late cases occur, the first year after SOT is the period of highest risk for histoplasmosis. In patients who survive the first month after diagnosis, treatment with an amphotericin formulation followed by an azole for 12 months is usually successful, with only rare relapse.
Keywords: fungal infection; histoplasmosis; solid organ transplant.
Figures
References
-
- Manos NE, Ferebee SH, Kerschbaum WF. Geographic variation in the prevalence of histoplasmin sensitivity. Dis Chest. 1956;29:649–68. - PubMed
-
- Wheat LJ, Connolly-Stringfield PA, Baker RL, et al. Disseminated histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: clinical findings, diagnosis and treatment, and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990;69:361–74. - PubMed
-
- Cuellar-Rodriguez J, Avery RK, Lard M, et al. Histoplasmosis in solid organ transplant recipients: 10 years of experience at a large transplant center in an endemic area. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:710–6. - PubMed
-
- Davies SF, Sarosi GA, Peterson PK, et al. Disseminated histoplasmosis in renal transplant recipients. Am J Surg. 1979;137:686–91. - PubMed
-
- Freifeld AG, Iwen PC, Lesiak BL, Gilroy RK, Stevens RB, Kalil AC. Histoplasmosis in solid organ transplant recipients at a large midwestern university transplant center. Transpl Infect Dis. 2005;7:109–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical