Tumor suppressor p16INK4A is necessary for survival of cervical carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 24046371
- PMCID: PMC3791710
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1310432110
Tumor suppressor p16INK4A is necessary for survival of cervical carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
The tumor suppressor p16(INK4A) inhibits formation of enzymatically active complexes of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) with D-type cyclins. Oncogenic stress induces p16(INK4A) expression, which in turn triggers cellular senescence through activation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. Subversion of oncogene-induced senescence is a key step during cancer development, and many tumors have lost p16(INK4A) activity by mutation or epigenetic silencing. Human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated tumors express high levels of p16(INK4A) in response to E7 oncoprotein expression. Induction of p16(INK4A) expression is not a consequence of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor inactivation but is triggered by a cellular senescence response and is mediated by epigenetic derepression through the H3K27-specific demethylase (KDM)6B. HPV E7 expression causes an acute dependence on KDM6B expression for cell survival. The p16(INK4A) tumor suppressor is a critical KDM6B downstream transcriptional target and its expression is critical for cell survival. This oncogenic p16(INK4A) activity depends on inhibition of CDK4/CDK6, suggesting that in cervical cancer cells where retinoblastoma tumor suppressor is inactivated, CDK4/CDK6 activity needs to be inhibited in order for cells to survive. Finally, we note that HPV E7 expression creates a unique cellular vulnerability to small-molecule KDM6A/B inhibitors.
Keywords: apoptosis; biomarker; cancer therapy; synthetic lethality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


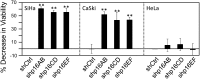
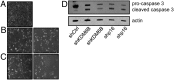

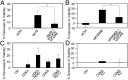
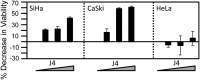

References
-
- Schwartz YB, Pirrotta V. Polycomb silencing mechanisms and the management of genomic programmes. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8(1):9–22. - PubMed
-
- Tolhuis B, et al. Genome-wide profiling of PRC1 and PRC2 Polycomb chromatin binding in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Genet. 2006;38(6):694–699. - PubMed
-
- Lund AH, van Lohuizen M. Epigenetics and cancer. Genes Dev. 2004;18(19):2315–2335. - PubMed
-
- Plath K, et al. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in X inactivation. Science. 2003;300(5616):131–135. - PubMed
-
- Schuettengruber B, Cavalli G. Recruitment of polycomb group complexes and their role in the dynamic regulation of cell fate choice. Development. 2009;136(21):3531–3542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

