Classics in chemical neuroscience: clozapine
- PMID: 24047509
- PMCID: PMC3715841
- DOI: 10.1021/cn400121z
Classics in chemical neuroscience: clozapine
Abstract
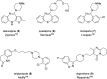
Clozapine was the first true breakthrough in schizophrenia treatment since the discovery of chlorpromazine in 1950, effectively treating positive, negative, and some cognitive symptoms, as well as possessing unprecedented efficacy in treatment-resistant patients. Despite over 30 years of intense study, the precise molecular underpinnings that account for clozapine's unique efficacy remain elusive. In this Viewpoint, we will showcase the history and importance of clozapine to neuroscience in general, as well as for the treatment of schizophrenia, and review the synthesis, pharmacology, drug metabolism, and adverse events of clozapine.
Figures
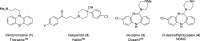


References
-
- Weinberger D. R., and Harrison P. J., Eds., (2011) Schizophrenia, 3rd ed., Wiley-Blackwell Publishing, Ltd., Oxford, UK.
-
- Carlsson A.; Lindquist M. (1963) Effect of chlorpromazine or haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxytyramine and normethanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 20, 140–144. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen N. C. (2000) Schizophrenia: the fundamental questions. Brain Res. Rev. 31, 106–112. - PubMed
-
- Karayiorgou M. (2001) Genetic aspects of schizophrenia. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 1, 158–163.
-
- Seeman P.; Lee T.; Chau-Wong M.; Wong K. (1976) Antipsychotic drug doses and neuroleptic/dopamine receptors. Nature 261, 717–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

