Oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) is required for the perinuclear localization of intra-Golgi v-SNAREs
- PMID: 24048449
- PMCID: PMC3826991
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E13-05-0250
Oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) is required for the perinuclear localization of intra-Golgi v-SNAREs
Abstract
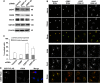
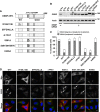
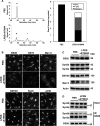
Oxysterol-binding protein (OSBP) and OSBP-related proteins (ORPs) have been implicated in the distribution of sterols among intracellular organelles. OSBP regulates the Golgi cholesterol level, but how it relates to Golgi function is elusive. Here we report that OSBP is essential for the localization of intra-Golgi soluble vesicle N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion attachment protein receptors (v-SNAREs). Depletion of OSBP by small interfering RNA causes mislocalization of intra-Golgi v-SNAREs GS28 and GS15 throughout the cytoplasm without affecting the perinuclear localization of Golgi target-SNARE syntaxin5 and reduces the abundance of a Golgi enzyme, mannosidase II (Man II). GS28 mislocalization and Man II reduction are also induced by cellular cholesterol depletion. Three domains of OSBP-an endoplasmic reticulum-targeting domain, a Golgi-targeting domain, and a sterol-binding domain-are all required for Golgi localization of GS28. Finally, GS28 mislocalization and Man II reduction in OSBP-depleted cells are largely restored by depletion of ArfGAP1, a regulator of the budding of coat protein complex (COP)-I vesicles. From these results, we postulate that Golgi cholesterol level, which is controlled by OSBP, is essential for Golgi localization of intra-Golgi v-SNAREs by ensuring proper COP-I vesicle transport.
Figures



Similar articles
-
GS15 forms a SNARE complex with syntaxin 5, GS28, and Ykt6 and is implicated in traffic in the early cisternae of the Golgi apparatus.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Oct;13(10):3493-507. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-01-0004. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12388752 Free PMC article.
-
Multisite phosphorylation of oxysterol-binding protein regulates sterol binding and activation of sphingomyelin synthesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Sep;23(18):3624-35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-04-0283. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22875984 Free PMC article.
-
Oxysterol-binding Protein Activation at Endoplasmic Reticulum-Golgi Contact Sites Reorganizes Phosphatidylinositol 4-Phosphate Pools.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 15;291(3):1336-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.682997. Epub 2015 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26601944 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Role of SNARE Protein GS28 in Vesicle Trafficking and Diseases.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023;24(4):288-295. doi: 10.2174/1389203724666230315143542. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2023. PMID: 36924089 Review.
-
Bridging the molecular and biological functions of the oxysterol-binding protein family.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Sep;75(17):3079-3098. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2795-y. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29536114 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of OSBP blocks retrograde trafficking by inducing partial Golgi degradation.Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Feb;21(2):203-214. doi: 10.1038/s41589-024-01653-x. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Nat Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 38907112
-
Dynamic assessment of PI4P metabolism using split GFP based sensors.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 21;15(1):30805. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15745-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40841827 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule localization microscopy reveals STING clustering at the trans-Golgi network through palmitoylation-dependent accumulation of cholesterol.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 11;15(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44317-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38212328 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-free assay implicates a role of sphingomyelin and cholesterol in STING phosphorylation.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 7;11(1):11996. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91562-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34099821 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi-Targeting Anticancer Natural Products.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 31;15(7):2086. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072086. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bligh EG, Dyer WJ. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959;37:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Churchward MA, Rogasevskaia T, Hofgen J, Bau J, Coorssen JR. Cholesterol facilitates the native mechanism of Ca2+-triggered membrane fusion. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4833–4848. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

