Treatment of Niemann--pick type C disease by histone deacetylase inhibitors
- PMID: 24048860
- PMCID: PMC3805865
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-013-0217-2
Treatment of Niemann--pick type C disease by histone deacetylase inhibitors
Abstract
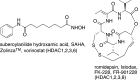
Niemann-Pick type C disease (NPC) is a devastating, recessive, inherited disorder that causes accumulation of cholesterol and other lipids in late endosomes and lysosomes. Mutations in 2 genes, NPC1 and NPC2, are responsible for the disease, which affects about 1 in 120,000 live births. About 95% of patients have mutations in NPC1, a large polytopic membrane protein that is normally found in late endosomes. More than 200 missense mutations in NPC1 have been found in NPC patients. The disease is progressive, typically leading to death before the age of 20 years, although some affected individuals live well into adulthood. The disease affects peripheral organs, including the liver, spleen, and lungs, but the most severe symptoms are associated with neurological disease. There are some palliative treatments that slow progression of NPC disease. Recently, it was found that histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors that are effective against HDACs 1, 2, and 3 can reduce the cholesterol accumulation in fibroblasts derived from NPC patients with mutations in NPC1. One example is vorinostat. As vorinostat is a Food and Drug Administration-approved drug for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, this opens up the possibility that HDAC inhibitors could be repurposed for treatment of this rare disease. The mechanism of action of the HDAC inhibitors requires further study, but these drugs increase the level of the NPC1 protein. This may be due to post-translational stabilization of the NPC1 protein, allowing it to be transported out of the endoplasmic reticulum.
Figures





References
-
- Niemann A. Ein unbekanntes Krankheitsbild. Jahrbuch für Kinderheilkunde. 1914;79:1–10.
-
- Der PL. Morbus Gaucher und die ihm ähnlichen Krankheiten (die lipoidzellige Splenohepatomegalie Typus Niemann und die diabetische Lipoidzellenhypoplasie der Milz. Ergebnisse der Inneren Medizin und Kinderheilkunde, Berlin. 1926;29:519–627.
-
- Crocker AC, Farber S. Niemann–Pick disease: a review of eighteen patients. Medicine. 1958;37:1–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

