Increased susceptibility to pulmonary Pseudomonas infection in Splunc1 knockout mice
- PMID: 24048904
- PMCID: PMC3839417
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202340
Increased susceptibility to pulmonary Pseudomonas infection in Splunc1 knockout mice
Abstract
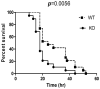
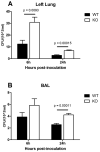
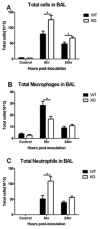
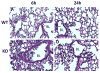
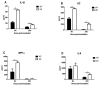
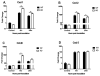
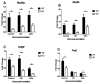
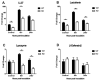
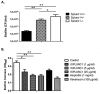
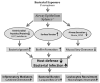
The airway epithelium is the first line of host defense against pathogens. The short palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (SPLUNC)1 protein is secreted in respiratory tracts and is a member of the bacterial/permeability increasing (BPI) fold-containing protein family, which shares structural similarities with BPI-like proteins. On the basis of its homology with BPIs and restricted expression of SPLUNC1 in serous cells of submucosal glands and surface epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract, SPLUNC1 is thought to possess antimicrobial activity in host defense. SPLUNC1 is also reported to have surfactant properties, which may contribute to anti-biofilm defenses. The objective of this study was to determine the in vivo functions of SPLUNC1 following Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and to elucidate the underlying mechanism by using a knockout (KO) mouse model with a genetic ablation of Splunc1. Splunc1 KO mice showed accelerated mortality and increased susceptibility to P. aeruginosa infection with significantly decreased survival rates, increased bacterial burdens, exaggerated tissue injuries, and elevated proinflammatory cytokine levels as compared with those of their wild-type littermates. Increased neutrophil infiltration in Splunc1 KO mice was accompanied by elevated chemokine levels, including Cxcl1, Cxcl2, and Ccl20. Furthermore, the expression of several epithelial secretory proteins and antimicrobial molecules was considerably suppressed in the lungs of Splunc1 KO mice. The deficiency of Splunc1 in mouse airway epithelium also results in increased biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa. Taken together, our results support that the ablation of Splunc1 in mouse airways affects the mucociliary clearance, resulting in decreased innate immune response during Pseudomonas-induced respiratory infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SPLUNC1/BPIFA1 contributes to pulmonary host defense against Klebsiella pneumoniae respiratory infection.Am J Pathol. 2013 May;182(5):1519-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.01.050. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23499554 Free PMC article.
-
Short palate, lung, and nasal epithelial clone-1 is a tightly regulated airway sensor in innate and adaptive immunity.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Jun;48(6):717-24. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0072OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23470624 Free PMC article.
-
α1-Antitrypsin promotes SPLUNC1-mediated lung defense against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in mice.Respir Res. 2013 Nov 9;14(1):122. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-122. Respir Res. 2013. PMID: 24209388 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifunctional Roles of Short Palate, Lung, and Nasal Epithelium Clone 1 in Regulating Airway Surface Liquid and Participating in Airway Host Defense.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2021 Apr;41(4):139-148. doi: 10.1089/jir.2020.0141. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2021. PMID: 33885339 Review.
-
Functional roles of SPLUNC1 in the innate immune response against Gram-negative bacteria.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Aug;39(4):1051-5. doi: 10.1042/BST0391051. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21787346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced therapeutic index of an antimicrobial peptide in mice by increasing safety and activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria.Sci Adv. 2020 May 1;6(18):eaay6817. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay6817. eCollection 2020 May. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32426473 Free PMC article.
-
CC16 drives VLA-2-dependent SPLUNC1 expression.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 20;14:1277582. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1277582. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38053993 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of ESKAPE pathogen biofilm formation by antimicrobial peptides WLBU2 and LL37.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 Nov;52(5):667-672. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.04.019. Epub 2018 May 10. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 29753132 Free PMC article.
-
Is the SPLUNC1-Orai1 axis a critical determinant of lung health?Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Jun 30;53(3):709-721. doi: 10.1042/BST20241029. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 40589325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced biofilm prevention activity of a SPLUNC1-derived antimicrobial peptide against Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 14;13(9):e0203621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203621. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30216370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di YP, Harper R, Zhao Y, Pahlavan N, Finkbeiner W, Wu R. Molecular cloning and characterization of spurt, a human novel gene that is retinoic acid-inducible and encodes a secretory protein specific in upper respiratory tracts. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2003;278:1165–1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

