Forward-planned intensity modulated radiation therapy using a cobalt source: A dosimetric study in breast cancer
- PMID: 24049319
- PMCID: PMC3775036
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.116367
Forward-planned intensity modulated radiation therapy using a cobalt source: A dosimetric study in breast cancer
Abstract
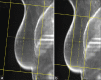
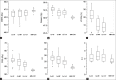
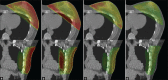
This analysis evaluates the feasibility and dosimetric results of a simplified intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) treatment using a cobalt-therapy unit for post-operative breast cancer. Fourteen patients were included. Three plans per patient were produced by a cobalt-60 source: A standard plan with two wedged tangential beams, a standard tangential plan optimized without the use of wedges and a plan based on the forward-planned "field-in-field" IMRT technique (Co-FinF) where the dose on each of the two tangential beams was split into two different segments and the two segments weight was determined with an iterative process. For comparison purposes, a 6-MV photon standard wedged tangential treatment plan was generated. Dmean, D98%, D2%, V95%, V107%, homogeneity, and conformity indices were chosen as parameters for comparison. Co-FinF technique improved the planning target volume dose homogeneity compared to other cobalt-based techniques and reduced maximum doses (D2%) and high-dose volume (V110%). Moreover, it showed a better lung and heart dose sparing with respect to the standard approach. The higher dose homogeneity may encourage the adoption of accelerated-hypofractionated treatments also with the cobalt sources. This approach can promote the spread of breast conservative treatment in developing countries.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; cobalt machine; intensity-modulated radiotherapy; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative dosimetric study on tangential photon beams, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and modulated electron radiotherapy (MERT) for breast cancer treatment.Phys Med Biol. 2003 Apr 7;48(7):909-24. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/48/7/308. Phys Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 12701895
-
[Dosimetric evaluation of intensity-modulated tangential beam versus conventional tangential irradiation for breast cancer].Ai Zheng. 2006 Jul;25(7):855-60. Ai Zheng. 2006. PMID: 16831277 Chinese.
-
Dosimetric comparison of intensity modulated radiotherapy isocentric field plans and field in field (FIF) forward plans in the treatment of breast cancer.J Med Phys. 2013 Jan;38(1):22-9. doi: 10.4103/0971-6203.106601. J Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23531607 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric study of inverse-planed intensity modulated, forward-planned intensity modulated and conventional tangential techniques in breast conserving radiotherapy.J Med Assoc Thai. 2008 Oct;91(10):1571-82. J Med Assoc Thai. 2008. PMID: 18972902
-
Robust optimization in lung treatment plans accounting for geometric uncertainty.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018 May;19(3):19-26. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12291. Epub 2018 Mar 10. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29524301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Breast telecobalt beam therapy using multi-isocentric technique.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020 Jan-Feb;25(1):79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2019.12.009. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020. PMID: 31908600 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the management of breast cancer in Africa.Infect Agent Cancer. 2017 Feb 14;12:13. doi: 10.1186/s13027-017-0124-y. eCollection 2017. Infect Agent Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28228841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bese NS, Munshi A, Budrukkar A, Elzawawy A, Perez CA Breast Health Global Initiative Radiation Therapy Focus Group. Breast radiation therapy guideline implementation in low- and middle-income countries. Cancer. 2008;113:2305–14. - PubMed
-
- Hurkmans CW, Meijer GJ, van Vliet-Vroegindeweij C, van der Sangen MJ, Cassee J. High-dose simultaneously integrated breast boost using intensity-modulated radiotherapy and inverse optimization. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66:923–30. - PubMed
-
- Singla R, King S, Albuquerque K, Creech S, Dogan N. Simultaneous-integrated boost intensity-modulated radiation therapy (SIB-IMRT) in the treatment of early-stage left-sided breast carcinoma. Med Dosim. 2006;31:190–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

