Plasticity of T helper cell subsets: Implications in periodontal disease
- PMID: 24049327
- PMCID: PMC3768177
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-124X.115637
Plasticity of T helper cell subsets: Implications in periodontal disease
Abstract
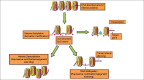
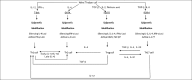
T helper (Th) cells have an important role in host defence as well in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Th cells differentiate from naive cells into various subsets, each of which is associated with a set of inducing and effector cytokines. Previously, it was thought that this differentiation was an irreversible event. Recent evidence suggest that even differentiated Th cells, retain the flexibility to transform from one lineage to another, a phenomenon referred to as plasticity. This plasticity is thought to be brought about by epigenetic modifications that are regulated by external and internal signals in the micro-environment of these cells. The factors and mechanisms which affect the plasticity of these cells and their potential role in the etio-pathogenesis of periodontal disease has been described in this article.
Keywords: Epigenetic modification; T helper cell; periodontal disease; plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic regulation of T-helper cell differentiation, memory, and plasticity in allergic asthma.Immunol Rev. 2017 Jul;278(1):8-19. doi: 10.1111/imr.12560. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28658556 Review.
-
Plasticity of CD4+ T cell lineage differentiation.Immunity. 2009 May;30(5):646-55. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.001. Immunity. 2009. PMID: 19464987 Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Dynamics of Th17 Differentiation and its Developmental Plasticity in the Intestinal Immune Response.Front Immunol. 2017 Mar 31;8:254. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00254. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28408906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic reprogramming of primary human T cells reveals functional plasticity in Th cell differentiation.J Immunol. 2003 Oct 1;171(7):3542-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.7.3542. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14500650
-
T-helper cells in the etiopathogenesis of periodontal disease: A mini review.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011 Jan;15(1):4-10. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.82255. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011. PMID: 21772714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. TH1 and TH2 cells: Different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–73. - PubMed
-
- Gemmell E, Yamazaki K, Seymour GJ. Destructive periodontitis lesions are determined by the nature of the lymphocytic response. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13:17–34. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima T, Ueki-Maruyama K, Oda T, Ohsawa Y, Ito H, Seymour GJ, et al. Regulatory T-cells infiltrate periodontal disease tissues. J Dent Res. 2005;84:639–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

