Distribution of MT1 melatonin receptor promoter-driven RFP expression in the brains of BAC C3H/HeN transgenic mice
- PMID: 24051358
- PMCID: PMC3873804
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155413507453
Distribution of MT1 melatonin receptor promoter-driven RFP expression in the brains of BAC C3H/HeN transgenic mice
Abstract
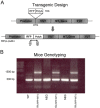
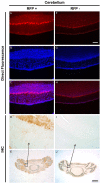
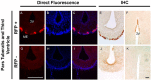
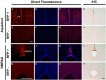
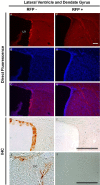
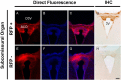
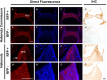
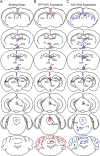
The pineal hormone melatonin activates two G-protein coupled receptors (MT1 and MT2) to regulate in part biological functions. The MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors are heterogeneously distributed in the mammalian brain including humans. In the mouse, only a few reports have assessed the expression of the MT1 melatonin receptor expression using 2-iodomelatonin binding, in situ hybridization and/or polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Here, we described a transgenic mouse in which red fluorescence protein (RFP) is expressed under the control of the endogenous MT1 promoter, by inserting RFP cDNA at the start codon of MTNR1a gene within a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) and expressing this construct as a transgene. The expression of RFP in the brain of this mouse was examined either directly under a fluorescent microscope or immunohistochemically using an antibody against RFP (RFP-MT1). RFP-MT1 expression was observed in many brain regions including the subcommissural organ, parts of the ependyma lining the lateral and third ventricles, the aqueduct, the hippocampus, the cerebellum, the pars tuberalis, the habenula and the habenula commissure. This RFP-MT1 transgenic model provides a unique tool for studying the distribution of the MT1 receptor in the brain of mice, its cell-specific expression and its function in vivo.
Keywords: C3H/HeN mice; MT1 melatonin receptors; RFP-MT1 promoter expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Aggelopoulos NC, Brown SJ, Demaine C, Harris NG, Jones HC. (1997). An abnormal distribution of melatonin receptors in the newborn rat with inherited prenatal hydrocephalus. Neurosci 80:669-673 - PubMed
-
- Al-Ghoul WM, Herman MD, Dubocovich ML. (1998). Melatonin receptor subtype expression in human cerebellum. Neuroreport 9:4063-4068 - PubMed
-
- Ambriz-Tututi M, Rocha-González HI, Cruz SL, Granados-Soto V. (2009). Melatonin: A hormone that modulates pain. Life Sci 84:489-498 - PubMed
-
- Andres KH, von During M, Veh RW. (1999). Subnuclear organization of the rat habenular complexes. J Comp Neurol 407:130-150 - PubMed
-
- Ayoub MA, Levoye A, Delagrange P, Jockers R. (2004). Preferential Formation of MT1/MT2 Melatonin Receptor Heterodimers with Distinct Ligand Interaction Properties Compared with MT2 Homodimers. Mol Pharmacol 66:312-321 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

