Opportunities for genomic clinical decision support interventions
- PMID: 24051479
- PMCID: PMC3858176
- DOI: 10.1038/gim.2013.128
Opportunities for genomic clinical decision support interventions
Figures
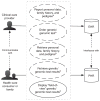
References
-
- Stanek EJ, Sanders CL, Taber KA, et al. Adoption of pharmacogenomic testing by US physicians: results of a nationwide survey. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012;91:450–458. - PubMed
-
- Brinner KA, Downing GJ American Health Information Community Personalized Health Care Workgroup. Advancing patient-centered pediatric care through health information exchange: update from the American Health Information Community Personalized Health Care Workgroup. Pediatrics. 2009;123(suppl 2):S122–S124. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman MA, Williams MS. Electronic medical records and personalized medicine. Hum Genet. 2011;130:33–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 LM009886/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006507/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006380/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U01 HG006388/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM105688/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T15LM007079/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- T15 LM007079/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM006910/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006382/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 HL065962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006828/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 3 U01 HG006828/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 3 U01 HG006382/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 LM008748/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006388/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006378/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

