Targeting fibroblast growth factor pathways in prostate cancer
- PMID: 24052019
- PMCID: PMC3926427
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1550
Targeting fibroblast growth factor pathways in prostate cancer
Abstract
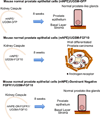
Advanced prostate cancer carries a poor prognosis and novel therapies are needed. Research has focused on identifying mechanisms that promote angiogenesis and cellular proliferation during prostate cancer progression from the primary tumor to bone-the principal site of prostate cancer metastases. One candidate pathway is the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) axis. Aberrant expression of FGF ligands and FGF receptors leads to constitutive activation of multiple downstream pathways involved in prostate cancer progression including mitogen-activated protein kinase, phosphoinositide 3-kinase, and phospholipase Cγ. The involvement of FGF pathways in multiple mechanisms relevant to prostate tumorigenesis provides a rationale for the therapeutic blockade of this pathway, and two small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors-dovitinib and nintedanib-are currently in phase II clinical development for advanced prostate cancer. Preliminary results from these trials suggest that FGF pathway inhibition represents a promising new strategy to treat castrate-resistant disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Information: PGC has served on a Novartis-sponsored advisory board for Dovitnib but did not receive any financial compensation.
Figures




References
-
- American, Cancer, Society. Cancer facts and figures 2012. 2012
-
- Kirby M, Hirst C, Crawford ED. Characterising the castration-resistant prostate cancer population: a systematic review. Int J Clin Pract. 2011;65:1180–1192. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal N, Sonpavde G, Sternberg CN. Novel molecular targets for the therapy of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2012;61:950–960. - PubMed
-
- Daniele G, Corral J, Molife LR, de Bono JS. FGF receptor inhibitors: role in cancer therapy. Curr Oncol Rep. 2012;14:111–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

