The HDAC inhibitor, MPT0E028, enhances erlotinib-induced cell death in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells
- PMID: 24052078
- PMCID: PMC3789188
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.330
The HDAC inhibitor, MPT0E028, enhances erlotinib-induced cell death in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells
Erratum in
-
Correction: The HDAC inhibitor, MPT0E028, enhances erlotinib induced cell death in EGFR-TKI-resistant NSCLC cells.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jul 9;15(7):490. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06794-4. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38982073 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
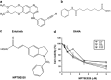
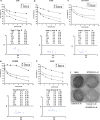
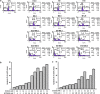
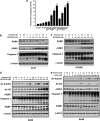
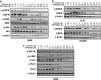
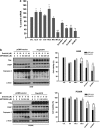
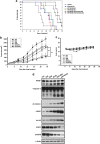
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which promotes cell survival and division, is found at abnormally high levels on the surface of many cancer cell types, including many cases of non-small cell lung cancer. Erlotinib (Tarceva), an oral small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is a so-called targeted drug that inhibits the tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR, and thus targets cancer cells with some specificity while doing less damage to normal cells. However, erlotinib resistance can occur, reducing the efficacy of this treatment. To develop more effective therapeutic interventions by overcoming this resistance problem, we combined the histone deacetylase inhibitor, MPT0E028, with erlotinib in an effort to increase their antitumor effects in erlotinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells. This combined treatment yielded significant growth inhibition, induced the expression of apoptotic proteins (PARP, γH2AX, and caspase-3), increased the levels of acetylated histone H3, and showed synergistic effects in vitro and in vivo. These effects were independent of the mutation status of the genes encoding EGFR or K-Ras. MPT0E028 synergistically blocked key regulators of the EGFR/HER2 signaling pathways, attenuating multiple compensatory pathways (e.g., AKT, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and c-MET). Our results indicate that this combination therapy might be a promising strategy for facilitating the effects of erlotinib monotherapy by activating various networks. Taken together, our data provide compelling evidence that MPT0E028 has the potential to improve the treatment of heterogeneous and drug-resistant tumors that cannot be controlled with single-target agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined inhibition of EZH2 and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2016 Jul;107(7):955-62. doi: 10.1111/cas.12957. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27116120 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of histone deacetylases sensitizes EGF receptor-TK inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer cells to erlotinib in vitro and in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;174(20):3608-3622. doi: 10.1111/bph.13961. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28749535 Free PMC article.
-
Combined therapy with mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor and Met kinase inhibitor for overcoming erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Oct;11(10):2149-57. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0195. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22844075
-
Combining onartuzumab with erlotinib inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer with activating EGFR mutations and HGF overexpression.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Feb;14(2):533-41. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0456. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25522765
-
Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor signalling pathway: A promising therapeutic option for COVID-19.Rev Med Virol. 2024 Jan;34(1):e2500. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2500. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Rev Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 38126937 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined inhibition of EZH2 and histone deacetylases as a potential epigenetic therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2016 Jul;107(7):955-62. doi: 10.1111/cas.12957. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27116120 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming acquired resistance of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells to osimertinib by combining osimertinib with the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589).Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;126(9):2024-2033. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32744. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31999837 Free PMC article.
-
Novel oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, MPT0E028, displays potent growth-inhibitory activity against human B-cell lymphoma in vitro and in vivo.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 10;6(7):4976-91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3213. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25669976 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative Activity of a New Quinazolin-4(3H)-One Derivative via Targeting Aurora Kinase A in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;15(6):698. doi: 10.3390/ph15060698. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745617 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Dysregulation in Cancer: Implications for Gene Expression and DNA Repair-Associated Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 7;26(13):6531. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136531. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650308 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:341–354. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Status of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists in the biology and treatment of cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2787–2799. - PubMed
-
- Garnis C, Lockwood WW, Vucic E, Ge Y, Girard L, Minna JD, et al. High resolution analysis of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by whole genome tiling path array CGH. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:1556–1564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

