Activation of the protein deacetylase SIRT6 by long-chain fatty acids and widespread deacylation by mammalian sirtuins
- PMID: 24052263
- PMCID: PMC3829447
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C113.511261
Activation of the protein deacetylase SIRT6 by long-chain fatty acids and widespread deacylation by mammalian sirtuins
Abstract
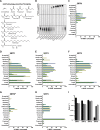
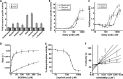
Mammalian sirtuins (SIRT1 through SIRT7) are members of a highly conserved family of NAD(+)-dependent protein deacetylases that function in metabolism, genome maintenance, and stress responses. Emerging evidence suggests that some sirtuins display substrate specificity toward other acyl groups attached to the lysine ε-amine. SIRT6 was recently reported to preferentially hydrolyze long-chain fatty acyl groups over acetyl groups. Here we investigated the catalytic ability of all sirtuins to hydrolyze 13 different acyl groups from histone H3 peptides, ranging in carbon length, saturation, and chemical diversity. We find that long-chain deacylation is a general feature of mammalian sirtuins, that SIRT1 and SIRT2 act as efficient decrotonylases, and that SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3, and SIRT4 can remove lipoic acid. These results provide new insight into sirtuin function and a means for cellular removal of an expanding list of endogenous lysine modifications. Given that SIRT6 is a poor deacetylase in vitro, but binds and prefers to hydrolyze long-chain acylated peptides, we hypothesize that binding of certain free fatty acids (FFAs) could stimulate deacetylation activity. Indeed, we demonstrate that several biologically relevant FFAs (including myristic, oleic, and linoleic acids) at physiological concentrations induce up to a 35-fold increase in catalytic efficiency of SIRT6 but not SIRT1. The activation mechanism is consistent with fatty acid inducing a conformation that binds acetylated H3 with greater affinity. Binding of long-chain FFA and myristoylated H3 peptide is mutually exclusive. We discuss the implications of discovering endogenous, small-molecule activators of SIRT6.
Keywords: Enzymology; Fatty Acids; Gene Regulation; Histone Deacetylase; Metabolism; Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids; Post-translational Modification; Sirtuins; coA.
Figures
References
-
- Mostoslavsky R., Chua K. F., Lombard D. B., Pang W. W., Fischer M. R., Gellon L., Liu P., Mostoslavsky G., Franco S., Murphy M. M., Mills K. D., Patel P., Hsu J. T., Hong A. L., Ford E., Cheng H. L., Kennedy C., Nunez N., Bronson R., Frendewey D., Auerbach W., Valenzuela D., Karow M., Hottiger M. O., Hursting S., Barrett J. C., Guarente L., Mulligan R., Demple B., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. (2006) Genomic instability and aging-like phenotype in the absence of mammalian SIRT6. Cell 124, 315–329 - PubMed
-
- Sebastián C., Zwaans B. M., Silberman D. M., Gymrek M., Goren A., Zhong L., Ram O., Truelove J., Guimaraes A. R., Toiber D., Cosentino C., Greenson J. K., MacDonald A. I., McGlynn L., Maxwell F., Edwards J., Giacosa S., Guccione E., Weissleder R., Bernstein B. E., Regev A., Shiels P. G., Lombard D. B., Mostoslavsky R. (2012) The histone deacetylase SIRT6 is a tumor suppressor that controls cancer metabolism. Cell 151, 1185–1199 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kanfi Y., Peshti V., Gil R., Naiman S., Nahum L., Levin E., Kronfeld-Schor N., Cohen H. Y. (2010) SIRT6 protects against pathological damage caused by diet-induced obesity. Aging Cell 9, 162–173 - PubMed
-
- Kanfi Y., Naiman S., Amir G., Peshti V., Zinman G., Nahum L., Bar-Joseph Z., Cohen H. Y. (2012) The sirtuin SIRT6 regulates lifespan in male mice. Nature 483, 218–221 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

