Human LilrB2 is a β-amyloid receptor and its murine homolog PirB regulates synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer's model
- PMID: 24052308
- PMCID: PMC3853120
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1242077
Human LilrB2 is a β-amyloid receptor and its murine homolog PirB regulates synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer's model
Abstract
Soluble β-amyloid (Aβ) oligomers impair synaptic plasticity and cause synaptic loss associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). We report that murine PirB (paired immunoglobulin-like receptor B) and its human ortholog LilrB2 (leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B2), present in human brain, are receptors for Aβ oligomers, with nanomolar affinity. The first two extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig) domains of PirB and LilrB2 mediate this interaction, leading to enhanced cofilin signaling, also seen in human AD brains. In mice, the deleterious effect of Aβ oligomers on hippocampal long-term potentiation required PirB, and in a transgenic model of AD, PirB not only contributed to memory deficits present in adult mice, but also mediated loss of synaptic plasticity in juvenile visual cortex. These findings imply that LilrB2 contributes to human AD neuropathology and suggest therapeutic uses of blocking LilrB2 function.
Figures
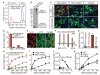

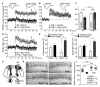
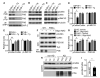
Comment in
-
Neuroscience. Promiscuous Alzheimer's amyloid: yet another partner.Science. 2013 Sep 20;341(6152):1354-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1244166. Science. 2013. PMID: 24052299 No abstract available.
-
Neurodegenerative disorders: a PIR-fect storm.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Nov;14(11):740-1. doi: 10.1038/nrn3616. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24088809 No abstract available.
-
Neurodegenerative disorders: A PIR-fect storm.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Nov;12(11):827. doi: 10.1038/nrd4159. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 24172329 No abstract available.
References
-
- Knafo S, et al. Cereb. Cortex. 2009;19:586–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 NS069811/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS069375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020016/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32EY020485/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P50AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AG041507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071666/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- EY02858/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS069375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EY002858/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 EY020485/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY002858/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08NS069811/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

