From bench to bedside: lessons learned in translating preclinical studies in cancer drug development
- PMID: 24052618
- PMCID: PMC3787906
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djt209
From bench to bedside: lessons learned in translating preclinical studies in cancer drug development
Abstract
The development of targeted agents in oncology has rapidly expanded over the past 2 decades and has led to clinically significant improvements in the treatment of numerous cancers. Unfortunately, not all success at the bench in preclinical experiments has translated to success at the bedside. As preclinical studies shift toward defining proof of mechanism, patient selection, and rational drug combinations, it is critical to understand the lessons learned from prior translational studies to gain an understanding of prior drug development successes and failures. By learning from prior drug development, future translational studies will provide more clinically relevant data, and the underlying hope is that the clinical success rate will improve and the treatment of patients with ineffective targeted therapy will be limited.
Figures
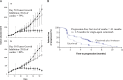


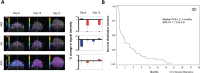
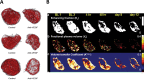

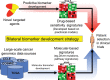
References
-
- Ozanne B, Richards CS, Hendler F, et al. Over-expression of the EGF receptor is a hallmark of squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 1986;149(1):9–14 - PubMed
-
- Sozzi G, Miozzo M, Tagliabue E, et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities and overexpression of receptors for growth factors in normal bronchial epithelium and tumor samples of lung cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1991;51(1):400–404 - PubMed
-
- Sato J, Kawamoto T, Le A, et al. Biological effects in vitro of monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal growth factor receptors. Mol Biol Med. 1983;1(5):511–529 - PubMed
-
- Gill GN, Kawamoto T, Cochet C, et al. Monoclonal anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies which are inhibitors of epidermal growth factor binding and antagonists of epidermal growth factor binding and antagonists of epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Bio Chem. 1984;259(12):7755–7760 - PubMed
-
- Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, et al. ZD1839 (Iressa): an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2002;62(20):5749–5754 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

