Sestrins orchestrate cellular metabolism to attenuate aging
- PMID: 24055102
- PMCID: PMC3858445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.08.018
Sestrins orchestrate cellular metabolism to attenuate aging
Abstract
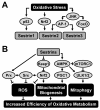
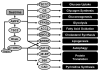
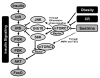
The Sestrins constitute a family of evolutionarily conserved stress-inducible proteins that suppress oxidative stress and regulate AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK)-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. By virtue of these activities, the Sestrins serve as important regulators of metabolic homeostasis. Accordingly, inactivation of Sestrin genes in invertebrates resulted in diverse metabolic pathologies, including oxidative damage, fat accumulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and muscle degeneration, that resemble accelerated tissue aging. Likewise, Sestrin deficiencies in mice led to accelerated diabetic progression upon obesity. Further investigation of Sestrin function and regulation should provide new insights into age-associated metabolic diseases, such as diabetes, myopathies, and cancer.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bae SH, Sung SH, Oh SY, Lim JM, Lee SK, Park YN, Lee HE, Kang D, Rhee SG. Sestrins activate Nrf2 by promoting p62-dependent autophagic degradation of Keap1 and prevent oxidative liver damage. Cell Metab. 2013;17:73–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA155120/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA172660/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P42-ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG024824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK082080/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK089503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG045432/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG024824/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118165/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013283/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG013283/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA118165/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK082080/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK089503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG045432/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CA155120/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172660/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
