The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs
- PMID: 24055342
- PMCID: PMC3843377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.027
The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs
Abstract
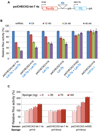
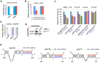
Abundantly expressed in fetal tissues and adult muscle, the developmentally regulated H19 long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) has been implicated in human genetic disorders and cancer. However, how H19 acts to regulate gene function has remained enigmatic, despite the recent implication of its encoded miR-675 in limiting placental growth. We noted that vertebrate H19 harbors both canonical and noncanonical binding sites for the let-7 family of microRNAs, which plays important roles in development, cancer, and metabolism. Using H19 knockdown and overexpression, combined with in vivo crosslinking and genome-wide transcriptome analysis, we demonstrate that H19 modulates let-7 availability by acting as a molecular sponge. The physiological significance of this interaction is highlighted in cultures in which H19 depletion causes precocious muscle differentiation, a phenotype recapitulated by let-7 overexpression. Our results reveal an unexpected mode of action of H19 and identify this lncRNA as an important regulator of the major let-7 family of microRNAs.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Boyerinas B, Park SM, Shomron N, Hedegaard MM, Vinther J, Andersen JS, Feig C, Xu J, Burge CB, Peter ME. Identification of let-7-regulated oncofetal genes. Cancer Res. 2008;68:2587–2591. - PubMed
-
- Braun T, Gautel M. Transcriptional mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle differentiation, growth and homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:349–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

