Lamina-associated polypeptide-1 interacts with the muscular dystrophy protein emerin and is essential for skeletal muscle maintenance
- PMID: 24055652
- PMCID: PMC3798056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.08.012
Lamina-associated polypeptide-1 interacts with the muscular dystrophy protein emerin and is essential for skeletal muscle maintenance
Abstract
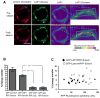
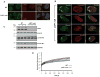
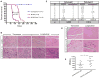
X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy is caused by loss of function of emerin, an integral protein of the inner nuclear membrane. Yet emerin null mice are essentially normal, suggesting the existence of a critical compensating factor. We show that the lamina-associated polypeptide1 (LAP1) interacts with emerin. Conditional deletion of LAP1 from striated muscle causes muscular dystrophy; this pathology is worsened in the absence of emerin. LAP1 levels are significantly higher in mouse than human skeletal muscle, and reducing LAP1 by approximately half in mice also induces muscle abnormalities in emerin null mice. Conditional deletion of LAP1 from hepatocytes yields mice that exhibit normal liver function and are indistinguishable from littermate controls. These results establish that LAP1 interacts physically and functionally with emerin and plays an essential and selective role in skeletal muscle maintenance. They also highlight how dissecting differences between mouse and human phenotypes can provide fundamental insights into disease mechanisms.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Bione S, Maestrini E, Rivella S, Mancini M, Regis S, Romeo G, Toniolo D. Identification of a novel X-linked gene responsible for Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1994;8:323–327. - PubMed
-
- Bonne G, Di Barletta MR, Varnous S, Bécane HM, Hammouda EH, Merlini L, Muntoni F, Greenberg CR, Gary F, Urtizberea JA, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1999;21:285–288. - PubMed
-
- Brodsky GL, Muntoni F, Miocic S, Sinagra G, Sewry C, Mestroni L. Lamin A/C gene mutation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy with variable skeletal muscle involvement. Circulation. 2000;101:473–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

