A distant homologue of the FlgT protein interacts with MotB and FliL and is essential for flagellar rotation in Rhodobacter sphaeroides
- PMID: 24056105
- PMCID: PMC3837945
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00760-13
A distant homologue of the FlgT protein interacts with MotB and FliL and is essential for flagellar rotation in Rhodobacter sphaeroides
Abstract
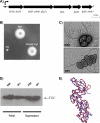
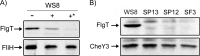
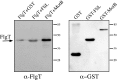
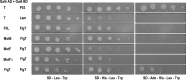
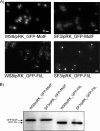
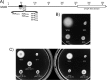
In this work, we describe a periplasmic protein that is essential for flagellar rotation in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. This protein is encoded upstream of flgA, and its expression is dependent on the flagellar master regulator FleQ and on the class III flagellar activator FleT. Sequence comparisons suggest that this protein is a distant homologue of FlgT. We show evidence that in R. sphaeroides, FlgT interacts with the periplasmic regions of MotB and FliL and with the flagellar protein MotF, which was recently characterized as a membrane component of the flagellum in this bacterium. In addition, the localization of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-MotF is completely dependent on FlgT. The Mot(-) phenotype of flgT cells was weakly suppressed by point mutants of MotB that presumably keep the proton channel open and efficiently suppress the Mot(-) phenotype of motF and fliL cells, indicating that FlgT could play an additional role beyond the opening of the proton channel. The presence of FlgT in purified filament-hook-basal bodies of the wild-type strain was confirmed by Western blotting, and the observation of these structures under an electron microscope showed that the basal bodies from flgT cells had lost the ring that covers the LP ring in the wild-type structure. Moreover, MotF was detected by immunoblotting in the basal bodies obtained from the wild-type strain but not from flgT cells. From these results, we suggest that FlgT forms a ring around the LP ring, which anchors MotF and stabilizes the stator complex of the flagellar motor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Living in a Foster Home: The Single Subpolar Flagellum Fla1 of Rhodobacter sphaeroides.Biomolecules. 2020 May 16;10(5):774. doi: 10.3390/biom10050774. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32429424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel component of the Rhodobacter sphaeroides Fla1 flagellum is essential for motor rotation.J Bacteriol. 2012 Nov;194(22):6174-83. doi: 10.1128/JB.00850-12. Epub 2012 Sep 7. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22961858 Free PMC article.
-
The flagellar protein FliL is essential for swimming in Rhodobacter sphaeroides.J Bacteriol. 2010 Dec;192(23):6230-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00655-10. Epub 2010 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20889747 Free PMC article.
-
The flagellar basal body-associated protein FlgT is essential for a novel ring structure in the sodium-driven Vibrio motor.J Bacteriol. 2010 Nov;192(21):5609-15. doi: 10.1128/JB.00720-10. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20729351 Free PMC article.
-
The bacterial flagellum and flagellar motor: structure, assembly and function.Adv Microb Physiol. 1991;32:109-72. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60007-7. Adv Microb Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1882727 Review.
Cited by
-
FliL and its paralog MotF have distinct roles in the stator activity of the Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellar motor.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Sep;118(3):223-243. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14964. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35808893 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of Vibrio FliL, a New Stomatin-like Protein That Assists the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Function.mBio. 2019 Mar 19;10(2):e00292-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00292-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30890608 Free PMC article.
-
Living in a Foster Home: The Single Subpolar Flagellum Fla1 of Rhodobacter sphaeroides.Biomolecules. 2020 May 16;10(5):774. doi: 10.3390/biom10050774. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32429424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of FlgP, an Essential Protein for Flagellar Assembly in Rhodobacter sphaeroides.J Bacteriol. 2019 Feb 11;201(5):e00752-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00752-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30559113 Free PMC article.
-
FliL association with flagellar stator in the sodium-driven Vibrio motor characterized by the fluorescent microscopy.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 24;8(1):11172. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29447-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30042401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berg HC. 2003. The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72:19–54 - PubMed
-
- Macnab RM. 2003. How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57:77–100 - PubMed
-
- Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K. 2008. Molecular motors of the bacterial flagella. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 18:693–701 - PubMed
-
- Terashima H, Kojima S, Homma M. 2008. Flagellar motility in bacteria: structure and function of flagellar motor. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 270:39–85 - PubMed
-
- Kojima S, Blair DF. 2004. The bacterial flagellar motor: structure and function of a complex molecular machine. Int. Rev. Cytol. 233:93–134 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

