GnRH pulse frequency-dependent differential regulation of LH and FSH gene expression
- PMID: 24056171
- PMCID: PMC3947649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.09.012
GnRH pulse frequency-dependent differential regulation of LH and FSH gene expression
Abstract
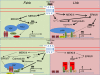
The pituitary gonadotropin hormones, FSH and LH, are essential for fertility. Containing an identical α-subunit (CGA), they are comprised of unique β-subunits, FSHβ and LHβ, respectively. These two hormones are regulated by the hypothalamic decapeptide, GnRH, which is released in a pulsatile manner from GnRH neurons located in the hypothalamus. Varying frequencies of pulsatile GnRH stimulate distinct signaling pathways and transcriptional machinery after binding to the receptor, GnRHR, on the cell surface of anterior pituitary gonadotropes. This ligand-receptor binding and activation orchestrates the synthesis and release of FSH and LH, in synergy with other effectors of gonadotropin production, such as activin, inhibin and steroids. Current research efforts aim to discover the mechanisms responsible for the decoding of the GnRH pulse signal by the gonadotrope. Modulating the response to GnRH has the potential to lead to new therapies for patients with altered gonadotropin secretion, such as those with hypothalamic amenorrhea or polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Keywords: FSH; GnRH; Gonadotrope; Gonadotropins; LH.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alarid ET, Windle JJ, Whyte DB, Mellon PL. Immortalization of pituitary cells at discrete stages of development by directed oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Development. 1996;122:3319–3329. - PubMed
-
- Belchetz PE, Plant TM, Nakai Y, Keogh EJ, Knobil E. Hypophysial responses to continuous and intermittent delivery of hypopthalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Science. 1978;202:631–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

