The eosinophil chemoattractant 5-oxo-ETE and the OXE receptor
- PMID: 24056189
- PMCID: PMC5710732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.09.001
The eosinophil chemoattractant 5-oxo-ETE and the OXE receptor
Abstract
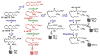
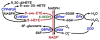
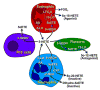
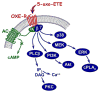
5-Oxo-ETE (5-oxo-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid) is formed from the 5-lipoxygenase product 5-HETE (5S-hydroxy-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid) by 5-hydroxyeicosanoid dehydrogenase (5-HEDH). The cofactor NADP(+) is a limiting factor in the synthesis of 5-oxo-ETE because of its low concentrations in unperturbed cells. Activation of the respiratory burst in phagocytic cells, oxidative stress, and cell death all dramatically elevate both intracellular NADP(+) levels and 5-oxo-ETE synthesis. 5-HEDH is widely expressed in inflammatory, structural, and tumor cells. Cells devoid of 5-lipoxygenase can synthesize 5-oxo-ETE by transcellular biosynthesis using inflammatory cell-derived 5-HETE. 5-Oxo-ETE is a chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes, and basophils and promotes the proliferation of tumor cells. However, its primary target appears to be the eosinophil, for which it is a highly potent chemoattractant. The actions of 5-oxo-ETE are mediated by the highly selective OXE receptor, which signals by activating various second messenger pathways through the release of the βγ-dimer from Gi/o proteins to which it is coupled. Because of its potent effects on eosinophils, 5-oxo-ETE may be an important mediator in asthma, and, because of its proliferative effects, may also contribute to tumor progression. Selective OXE receptor antagonists, which are currently under development, could be useful therapeutic agents in asthma and other allergic diseases.
Keywords: 12-HHT; 12-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid; 4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z-docosahexaenoic acid; 5,12-diHETE; 5,15-diHETE; 5-HEDH; 5-HEPE; 5-HETE; 5-HETrE; 5-HODE; 5-HpETE; 5-LO; 5-Lipoxygenase; 5-Oxo-ETE; 5-hydroxyeicosanoid dehydrogenase; 5-lipoxygenase; 5-oxo-12-HETE; 5-oxo-12S-hydroxy-6E,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5-oxo-15-HETE; 5-oxo-15S-hydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z,13E-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5-oxo-20-HETE; 5-oxo-20-hydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5-oxo-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z-eicosapentaenoic acid; 5-oxo-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5-oxo-6E,8Z,11Z-eicosatrienoic acid; 5-oxo-6E,8Z-octadecadienoic acid; 5-oxo-7-glutathionyl factor-8,11,14-eicosatrienoic acid; 5-oxo-EPE; 5-oxo-ETE; 5-oxo-ETrE; 5-oxo-ODE; 5S,12S-dihydroxy-6E,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5S,15S-dihydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z,13E-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5S-hydroperoxy-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5S-hydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z-eicosapentaenoic acid; 5S-hydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid; 5S-hydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z-eicosatrienoic acid; 5S-hydroxy-6E,8Z-octadecadienoic acid; 5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z-eicosapentaenoic acid; 5Z,8Z,11Z-eicosatrienoic acid; 5Z,8Z-octadecadienoic acid; Asthma; Chemoattractants; DHA; ECL; EPA; Eosinophils; FOG(7); G protein-coupled receptor; GPCR; Inflammation; LT; LXA(4); Mead acid; PAF; PI3K; PLC; PMA; PUFA; Sebaleic acid; StAR; eosinophil chemotactic lipid; leukotriene; lipoxin A(4); phorbol myristate acetate; phosphoinositide-3 kinase; phospholipase C; platelet-activating; polyunsaturated fatty acid; steroidogenic acute regulatory protein; uPAR; urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural requirements for activation of the 5-oxo-6E,8Z, 11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxo-ETE) receptor: identification of a mead acid metabolite with potent agonist activity.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 May;325(2):698-707. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.134908. Epub 2008 Feb 21. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18292294
-
Biological Roles of 5-Oxo-6,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic Acid and the OXE Receptor in Allergic Diseases: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum Update 2024.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2024;185(4):301-310. doi: 10.1159/000535560. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38176394 Review.
-
Substrate selectivity of 5-hydroxyeicosanoid dehydrogenase and its inhibition by 5-hydroxy-Delta6-long-chain fatty acids.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009 Apr;329(1):335-41. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.143453. Epub 2009 Jan 22. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009. PMID: 19164464 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the OXE receptor as a potential novel therapy for asthma.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;179:113930. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113930. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32240653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human neutrophils convert the sebum-derived polyunsaturated fatty acid Sebaleic acid to a potent granulocyte chemoattractant.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 25;283(17):11234-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709531200. Epub 2008 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18287092 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Trisomy 21-driven metabolite alterations are linked to cellular injuries in Down syndrome.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Mar 3;81(1):112. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05127-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38433139 Free PMC article.
-
Oxoeicosanoid signaling mediates early antimicrobial defense in zebrafish.Cell Rep. 2023 Jan 31;42(1):111974. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111974. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36640321 Free PMC article.
-
Detoxification Cytochrome P450s (CYPs) in Families 1-3 Produce Functional Oxylipins from Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids.Cells. 2022 Dec 24;12(1):82. doi: 10.3390/cells12010082. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles for lipids in non-apoptotic cell death.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Jul;23(7):1099-109. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.25. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26967968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and metabolomic changes in the proximal colon of pigs infected with Trichuris suis.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 30;10(1):12853. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69462-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32732949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borgeat P, Hamberg M, Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid and homo-gamma-linolenic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Monohydroxy acids from novel lipoxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1976;251:7816–20. - PubMed
-
- Borgeat P, Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Formation of a novel dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:2643–6. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN, Hamberg M, Samuelsson B. Trihydroxytetraenes: a novel series of compounds formed from arachidonic acid in human leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;118:943–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

