Fibroblast growth factor-2 signaling in neurogenesis and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 24057103
- PMCID: PMC4109802
- DOI: 10.1007/s11481-013-9501-5
Fibroblast growth factor-2 signaling in neurogenesis and neurodegeneration
Abstract
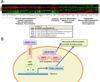
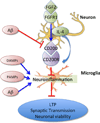
Fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2), also known as basic FGF, is a multi-functional growth factor. One of the 22-member FGF family, it signals through receptor tyrosine kinases encoding FGFR1-4. FGF2 activates FGFRs in cooperation with heparin or heparin sulfate proteoglycan to induce its pleiotropic effects in different tissues and organs, which include potent angiogenic effects and important roles in the differentiation and function of the central nervous system (CNS). FGF2 is crucial to development of the CNS, which explains its importance in adult neurogenesis. During development, high levels of FGF2 are detected from neurulation onwards. Moreover, developmental expression of FGF2 and its receptors is temporally and spatially regulated, concurring with development of specific brain regions including the hippocampus and substantia nigra pars compacta. In adult neurogenesis, FGF2 has been implicated based on its expression and regulation of neural stem and progenitor cells in the neurogenic niches, the subventricular zone (SVZ) and the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the hippocampal dentate gyrus. FGFR1 signaling also modulates inflammatory signaling through the surface glycoprotein CD200, which regulates microglial activation. Because of its importance in adult neurogenesis and neuroinflammation, manipulation of FGF2/FGFR1 signaling has been a focus of therapeutic development for neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and traumatic brain injury. Novel strategies include intranasal administration of FGF2, administration of an NCAM-derived FGFR1 agonist, and chitosan-based nanoparticles for the delivery of FGF2 in pre-clinical animal models. In this review, we highlight current research towards therapeutic interventions targeting FGF2/FGFR1 in neurodegenerative disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of developmental nuclear fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 signaling and neurogenesis in adult brain by α7 nicotinic receptor agonist.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013 Oct;2(10):776-88. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0103. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 24014683 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic model for FGF, FGFR, and proteoglycan signal transduction complex assembly.Biochemistry. 2004 Apr 27;43(16):4724-30. doi: 10.1021/bi0352320. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15096041
-
The FGF-2/FGFRs neurotrophic system promotes neurogenesis in the adult brain.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Aug;116(8):995-1005. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0207-z. Epub 2009 Mar 17. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19291360 Review.
-
Peptides derived from specific interaction sites of the fibroblast growth factor 2-FGF receptor complexes induce receptor activation and signaling.J Neurochem. 2010 Jul;114(1):74-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06718.x. Epub 2010 Mar 31. J Neurochem. 2010. PMID: 20374425
-
α7 nicotinic receptor agonist reactivates neurogenesis in adult brain.Biochem Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;86(8):1099-104. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.07.028. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23933384 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular markers associated with perineural invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2020 Oct;20(4):5. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11866. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32774479 Free PMC article.
-
Help-me signaling: Non-cell autonomous mechanisms of neuroprotection and neurorecovery.Prog Neurobiol. 2017 May;152:181-199. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Prog Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27079786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The FGF/FGFR system in the microglial neuroinflammation with Borrelia burgdorferi: likely intersectionality with other neurological conditions.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Jan 17;20(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02681-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36650549 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Microarray-Based Global Gene Expression Profiling in Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells Predicts the Potential of Microalgae-Derived Squalene for the Nervous System and Metabolic Health.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 27;10(1):48. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010048. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 35052729 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNA-sequencing identifies various proportions of excitatory and inhibitory neurons in cultured human fetal brain cortical tissues.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 28;17:1177747. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1177747. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37449269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burgess WH, Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. - PubMed
-
- Jaye M, Schlessinger J, Dionne CA. Fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases: molecular analysis and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992;1135(2):185–199. - PubMed
-
- Tao Y, Black IB, DiCicco-Bloom E. Neurogenesis in neonatal rat brain is regulated by peripheral injection of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) J Comp Neurol. 1996;376(4):653–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

