Magnetic Resonance Image Example-Based Contrast Synthesis
- PMID: 24058022
- PMCID: PMC3955746
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2282126
Magnetic Resonance Image Example-Based Contrast Synthesis
Abstract
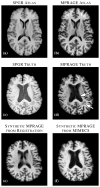
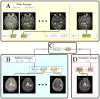
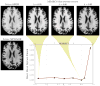
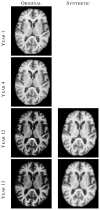
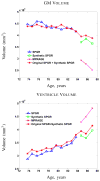
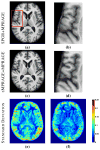
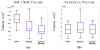
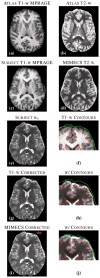
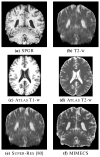
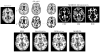
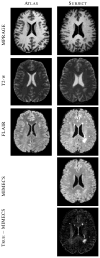
The performance of image analysis algorithms applied to magnetic resonance images is strongly influenced by the pulse sequences used to acquire the images. Algorithms are typically optimized for a targeted tissue contrast obtained from a particular implementation of a pulse sequence on a specific scanner. There are many practical situations, including multi-institution trials, rapid emergency scans, and scientific use of historical data, where the images are not acquired according to an optimal protocol or the desired tissue contrast is entirely missing. This paper introduces an image restoration technique that recovers images with both the desired tissue contrast and a normalized intensity profile. This is done using patches in the acquired images and an atlas containing patches of the acquired and desired tissue contrasts. The method is an example-based approach relying on sparse reconstruction from image patches. Its performance in demonstrated using several examples, including image intensity normalization, missing tissue contrast recovery, automatic segmentation, and multimodal registration. These examples demonstrate potential practical uses and also illustrate limitations of our approach.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subject Specific Sparse Dictionary Learning for Atlas based Brain MRI Segmentation.Mach Learn Med Imaging. 2014;8679:248-255. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10581-9_31. Mach Learn Med Imaging. 2014. PMID: 25383394 Free PMC article.
-
A compressed sensing approach for MR tissue contrast synthesis.Inf Process Med Imaging. 2011;22:371-83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-22092-0_31. Inf Process Med Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21761671 Free PMC article.
-
MR image synthesis by contrast learning on neighborhood ensembles.Med Image Anal. 2015 Aug;24(1):63-76. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2015.05.002. Epub 2015 May 18. Med Image Anal. 2015. PMID: 26072167 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Multiplied, Added, Subtracted and/or FiTted Inversion Recovery (MASTIR) pulse sequences.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020 Jun;10(6):1334-1369. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-568. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 32550142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of atlas-based segmentation for magnetic resonance brain images.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2011 Dec;104(3):e158-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2011.07.015. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2011. PMID: 21871688 Review.
Cited by
-
A multimodal deep learning approach for the prediction of cognitive decline and its effectiveness in clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 21;14(1):105. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02819-w. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38383536 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Impact of Intensity Normalization on MR Image Synthesis.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2019 Mar;10949:109493H. doi: 10.1117/12.2513089. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2019. PMID: 31551645 Free PMC article.
-
Brain lesion segmentation through image synthesis and outlier detection.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 Sep 8;16:643-658. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.09.003. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 29868438 Free PMC article.
-
A high-generalizability machine learning framework for predicting the progression of Alzheimer's disease using limited data.NPJ Digit Med. 2022 Apr 12;5(1):43. doi: 10.1038/s41746-022-00577-x. NPJ Digit Med. 2022. PMID: 35414651 Free PMC article.
-
Subject Specific Sparse Dictionary Learning for Atlas based Brain MRI Segmentation.Mach Learn Med Imaging. 2014;8679:248-255. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10581-9_31. Mach Learn Med Imaging. 2014. PMID: 25383394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bezdek JC, Hall LO, Clarke LP. Review of MR image segmentation techniques using pattern recognition. Med Physics. 1993;20(4):1033–1048. - PubMed
-
- Bazin PL, Pham DL. Topology-preserving tissue classification of magnetic resonance brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2007 Apr;26(4):487–496. - PubMed
-
- Clark KA, Woods RP, Rottenberg DA, Toga AW, Mazziotta JC. Impact of acquisition protocols and processing streams on tissue segmentation of T1 weighted MR images. NeuroImage. 2006;29(1):185–202. - PubMed
-
- Boesen K, Rehm K, Schaper K, Stoltzner S, Woods R, Lüders E, Rottenberg D. Quantitative comparison of four brain extraction algorithms. NeuroImage. 2004 Jul;22(3):1255–1261. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

