H(2)S inhibits hyperglycemia-induced intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activation via attenuation of reactive oxygen species generation
- PMID: 24058553
- PMCID: PMC3772925
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074366
H(2)S inhibits hyperglycemia-induced intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activation via attenuation of reactive oxygen species generation
Abstract
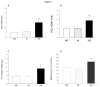
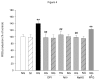
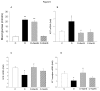
Decrease in endogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) was reported to participate in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy (DN). This study is aimed at exploring the relationship between the abnormalities in H2S metabolism, hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and the activation of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Cultured renal mesangial cells (MCs) and streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic rats were used for the studies. The expressions of angiotensinogen (AGT), angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II (Ang II) type I receptor (AT1), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and collagen IV were measured by real time PCR and Western blot. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was assessed by fluorescent probe assays. Cell proliferation was analyzed by 5'-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine incorporation assay. Ang II concentration was measured by an enzyme immunoassay. AGT, ACE and AT1 receptor mRNA levels and Ang II concentration were increased in high glucose (HG) -treated MCs, the cell proliferation rate and the production of TGF-β1 and of collagen IV productions were also increased. The NADPH oxidase inhibitor diphenylenechloride iodonium (DPI) was able to reverse the HG-induced RAS activation and the changes in cell proliferation and collagen synthesis. Supplementation of H2S attenuated HG-induced elevations in ROS and RAS activation. Blockade on H2S biosynthesis from cystathione-γ-lyase (CSE) by DL-propargylglycine (PPG) resulted in effects similar to that of HG treatment. In STZ-induced diabetic rats, the changes in RAS were also reversed by H2S supplementation without affecting blood glucose concentration. These data suggested that the decrease in H2S under hyperglycemic condition leads to an imbalance between oxidative and reductive species. The increased oxidative species results in intrarenal RAS activation, which, in turn, contributes to the pathogenesis of renal dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Ritz E, Rychlík I, Locatelli F, Halimi S (1999) End-stage renal failure in type 2 diabetes: A medical catastrophe of worldwide dimensions. Am J Kidney Dis 34: 795-808. doi:10.1016/S0272-6386(99)70035-1. PubMed: 10561134. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davis LK, Rodgers BD, Kelley KM (2008) Angiotensin II- and glucose-stimulated extracellular matrix production: mediation by the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis in a murine mesangial cell line. Endocrine 33: 32-39. doi:10.1007/s12020-008-9055-0. PubMed: 18392786. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Steffes MW, Osterby R, Chavers B, Mauer SM (1989) Mesangial expansion as a central mechanism for loss of kidney function in diabetic patients. Diabetes 38: 1077-1081. doi:10.2337/diabetes.38.9.1077. PubMed: 2670639. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szabo C (2012) Roles of hydrogen sulfide in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Antioxid Redox Signal 17: 68-80. doi:10.1089/ars.2011.4451. PubMed: 22149162. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang G, Wu L, Bryan S, Khaper N, Mani S et al. (2010) Cystathionine gamma-lyase deficiency and overproliferation of smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res 86: 487-495. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvp420. PubMed: 20051385. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

