Targeting the tumor microenvironment: JAK-STAT3 signaling
- PMID: 24058812
- PMCID: PMC3710325
- DOI: 10.4161/jkst.23828
Targeting the tumor microenvironment: JAK-STAT3 signaling
Abstract
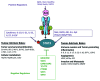
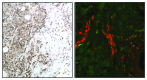
Persistent JAK-STAT3 signaling is implicated in many aspects of tumorigenesis. Apart from its tumor-intrinsic effects, STAT3 also exerts tumor-extrinsic effects, supporting tumor survival and metastasis. These involve the regulation of paracrine cytokine signaling, alterations in metastatic sites rendering these permissive for the growth of cancer cells and subversion of host immune responses to create an immunosuppressive environment. Targeting this signaling pathway is considered a novel promising therapeutic approach, especially in the context of tumor immunity. In this article, we will review to what extent JAK-STAT3-targeted therapies affect the tumor microenvironment and whether the observed effects underlie responsiveness to therapy.
Keywords: IL-6; JAK-STAT3 signaling; targeted therapies; tumor microenvironment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insights into IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer therapy.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025 Jan 17:S1359-6101(25)00003-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2025.01.003. Online ahead of print. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025. PMID: 39893129 Review.
-
The JAK/STAT3 axis: A comprehensive drug target for solid malignancies.Semin Cancer Biol. 2017 Aug;45:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017. PMID: 28647610 Review.
-
Jak Stat signaling and cancer: Opportunities, benefits and side effects of targeted inhibition.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Aug 15;451:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.05.033. Epub 2017 May 30. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28576744 Review.
-
Epigenetic modification of SOCS-1 differentially regulates STAT3 activation in response to interleukin-6 receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling through JAK and/or MEK in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Jan;5(1):8-19. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0069. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16432158
-
Targeting JAK kinase in solid tumors: emerging opportunities and challenges.Oncogene. 2016 Feb 25;35(8):939-51. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.150. Epub 2015 May 18. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25982279 Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing CDC25A inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells by downregulating IL‑6 in vitro and in vivo.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Mar;45(3):743-752. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4461. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31922225 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the Type II Chaperonin, TRiC/CCT, to Oncogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 6;16(11):26706-20. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125975. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26561808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RECK controls breast cancer metastasis by modulating a convergent, STAT3-dependent neoangiogenic switch.Oncogene. 2015 Apr 23;34(17):2189-203. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.175. Epub 2014 Jun 16. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24931164 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Implications for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 14;13(14):3526. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143526. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of STAT3 signaling as critical molecular event in HUC-MSCs suppressed Glioblastoma Cells.J Cancer. 2023 Feb 27;14(4):611-627. doi: 10.7150/jca.77905. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37057281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sommer J, Effenberger T, Volpi E, Waetzig GH, Bernhardt M, Suthaus J, et al. Constitutively active mutant gp130 receptor protein from inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma is inhibited by an anti-gp130 antibody that specifically neutralizes interleukin 11 signaling. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:13743–51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.349167. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
