Advancing our understanding of the human microbiome using QIIME
- PMID: 24060131
- PMCID: PMC4517945
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407863-5.00019-8
Advancing our understanding of the human microbiome using QIIME
Abstract
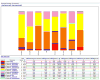
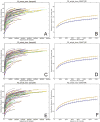
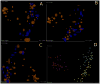
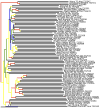
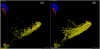
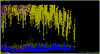
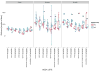
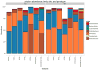
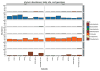
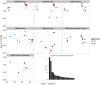
High-throughput DNA sequencing technologies, coupled with advanced bioinformatics tools, have enabled rapid advances in microbial ecology and our understanding of the human microbiome. QIIME (Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology) is an open-source bioinformatics software package designed for microbial community analysis based on DNA sequence data, which provides a single analysis framework for analysis of raw sequence data through publication-quality statistical analyses and interactive visualizations. In this chapter, we demonstrate the use of the QIIME pipeline to analyze microbial communities obtained from several sites on the bodies of transgenic and wild-type mice, as assessed using 16S rRNA gene sequences generated on the Illumina MiSeq platform. We present our recommended pipeline for performing microbial community analysis and provide guidelines for making critical choices in the process. We present examples of some of the types of analyses that are enabled by QIIME and discuss how other tools, such as phyloseq and R, can be applied to expand upon these analyses.
Keywords: Highthroughput sequencing; Microbial community analyses; Microbial ecology; Microbiome; QIIME.
© 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

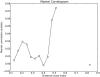
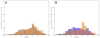
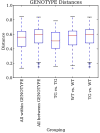
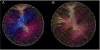


References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403–410. - PubMed
-
- Allaire J, Horner J, Marti V, Porte N. markdown: Markdown rendering for R. from http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=markdown.
-
- Atlas RM, Bartha R. Microbial ecology : fundamentals and applications. 4. Menlo Park, Calif: Harlow: Benjamin/Cummings; 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

