Comparison of endoscopic therapies and surgical resection in patients with early esophageal cancer: a population-based study
- PMID: 24060519
- PMCID: PMC4042678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.08.002
Comparison of endoscopic therapies and surgical resection in patients with early esophageal cancer: a population-based study
Abstract
Background: Outcome data comparing endoscopic eradication therapy (EET) and esophagectomy are limited in patients with early esophageal cancer (EC).
Objective: To compare overall survival and EC-related mortality in patients with early EC treated with EET and esophagectomy.
Design and setting: Population-based study.
Patients: Patients with early EC (stages T0 and T1) were identified from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database (1998-2009). Demographics, tumor specific data, and survival were compared. Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to evaluate the association between treatment and EC-specific mortality.
Intervention: EET and esophagectomy.
Main outcome measurements: Mid- (2 years) and long- (5 years) term overall survival and EC-specific mortality, outcomes based on histology and stage, treatment patterns, and predictors of cancer-specific mortality.
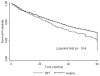
Results: A total of 430 (21%) and 1586 (79%) patients underwent EET and esophagectomy, respectively. There was no difference in the 2-year (EET: 10.5% vs esophagectomy: 12.7%, P = .27).and 5-year (EET: 36.7% vs esophagectomy: 42.8%, P = .16) EC-related mortality rates between the 2 groups. EET patients had higher mortality rates attributed to non-EC causes (5 years: 46.6% vs 20.6%, P < .001). Similar results were noted when comparisons were limited to patients with stage T0 and T1a disease and esophageal adenocarcinoma. There was no difference in EC-specific mortality in the EET compared with the surgery group (hazard ratio 1.4; 95% confidence interval, 0.9-2.03). Variables associated with mortality were older age, year of diagnosis, radiation therapy, higher stage, and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Limitations: Comorbidities and recurrence rates were not available.
Conclusions: This population-based study demonstrates comparable mid- and long-term EC-related mortality in patients with early EC undergoing EET and surgical resection.
Keywords: CI; EAC; EC; EET; ESCC; HR; SEER; Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results; confidence interval; endoscopic eradication therapy; esophageal adenocarcinoma; esophageal cancer; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; hazard ratio.
Copyright © 2014 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pohl H, Welch HG. The role of overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:142–6. - PubMed
-
- Pohl H, Sirovich B, Welch HG. Esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence: are we reaching the peak? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:1468–70. - PubMed
-
- Das A, Singh V, Fleischer DE, et al. A comparison of endoscopic treatment and surgery in early esophageal cancer: an analysis of surveillance epidemiology and end results data. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:1340–5. - PubMed
-
- Rice TW, Rusch VW, Ishwaran H, et al. Cancer of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: data-driven staging for the seventh edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer/International Union Against Cancer Cancer Staging Manuals. Cancer. 2010;116:3763–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical